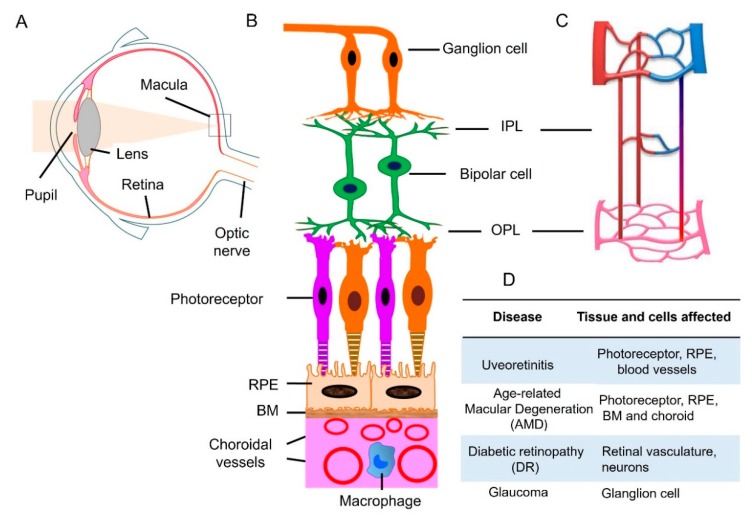
Figure 1.
Retinal neuronal and vascular structure and retinal disease. (A) Diagram of a human eye. Light passes through the pupil and is focused by lens onto macula of the retinal layer at the back of the eye. (B) Retina consists of three layers of neurons, photoreceptor, bipolar, and ganglion cells. The retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) monolayer together with Bruch’s membrane (BM) form outer blood retinal barrier that separates the neuroretina from the choroid. Choroidal circulation provides oxygen and nutrients to outer retina. (C) The retina has an interconnected network of three vascular layers located in the ganglion cell/nerve fiber layer, inner plexiform layer (IPL), and outer plexiform layer (OPL). (D) retinal tissue and cells that are affected under different disease conditions. Adapted from reference [17].