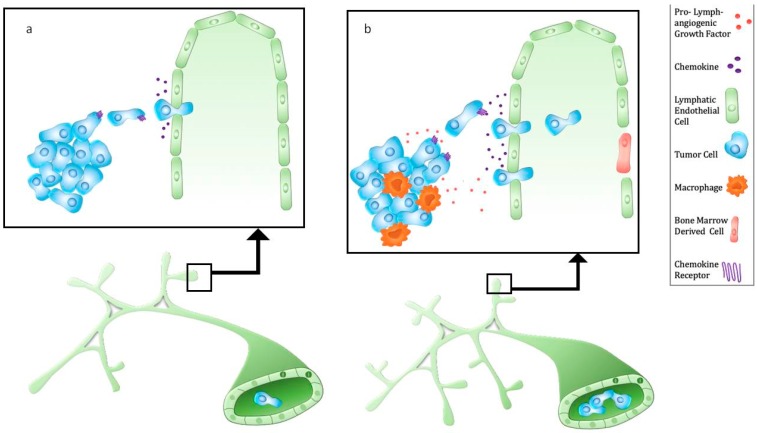
Figure 1.
Metastasis via tumor-associated lymphatic vessels. (a) Tumor cells express chemokine receptors (e.g., CXCR4, CCR7) which bind chemokines produced by lymphatic endothelium (e.g., CXCL12, CCL21). Lymphatic vessel-derived CCL21 attracts cancer cells that can enter initial lymphatic vessels through interendothelial cell gaps. (b) Cancer cells and tumor-associated macrophages secrete pro-lymphangiogenic factors such as VEGF-C, leading to an increase initial lymphatic vessel density and collecting lymphatic vessel diameter. In addition, VEGF-C upregulates CCL21 and increases lymphatic vessel permeability, resulting in enhanced lymphatic metastasis. Of note, bone marrow derived cells can closely associate with or incorporate into lymphatic vessels.