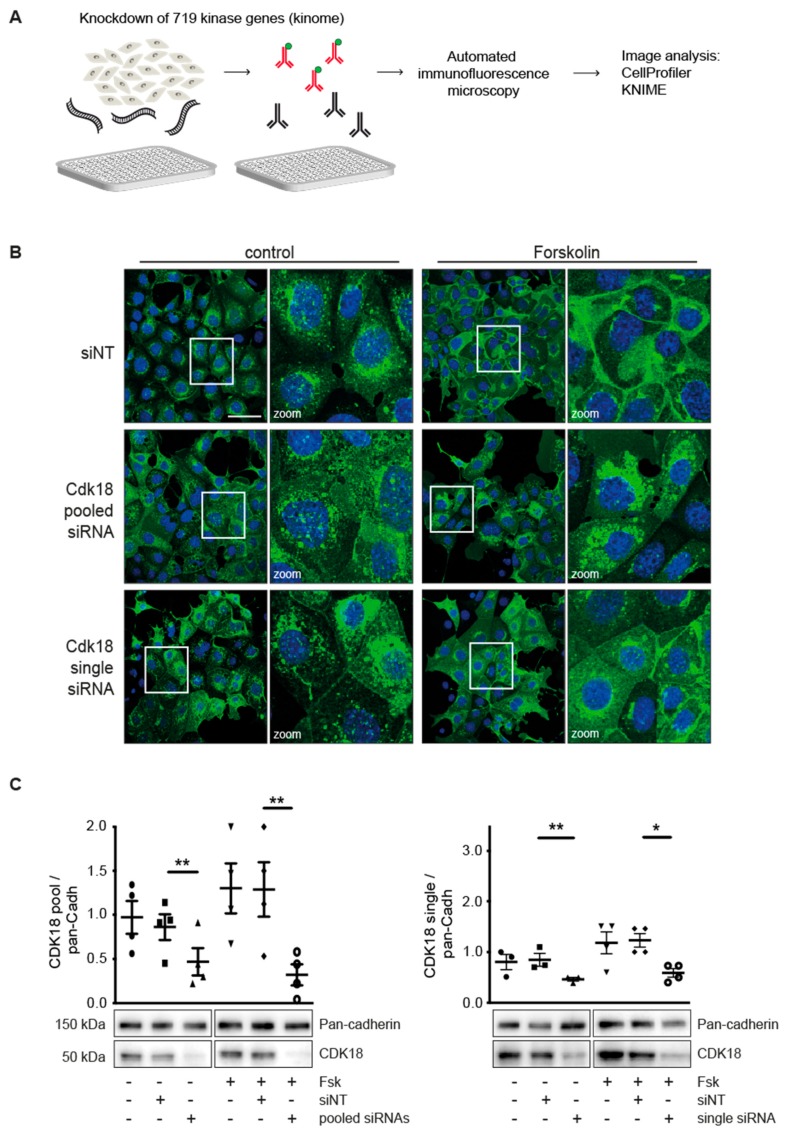
Figure 1.
CDK18 is necessary for the cAMP-induced redistribution of AQP2 from intracellular vesicles to the plasma membrane. (A) Schematic representation of the Kinome-wide siRNA screening approach. MCD4 cells were seeded in 384-well microtiter plates and the expression of 719 kinases was knocked down each with a pool of four siRNAs. The effects of the knockdown on the localization of AQP2 were detected with specific anti-AQP2 and secondary Cy3-coupled antibodies and automated immunofluorescence microscopic analysis. Image analysis was carried out with CellProfiler and KNIME software. (B) MCD4 cells were treated with 50 nM non-targeting siRNA (siNT), a pool of four different or a single CDK18 siRNA. The cells were treated with forskolin (Fsk; 30 µM, 60 min) or were left unstimulated (control) and the localization of AQP2 was analyzed with a confocal laser scanning microscope (40× magnification). AQP2 is in green and nuclei are in blue. Shown are representative images from n ≥ 3 independent experiments per condition; scale bar, 50 µm. (C) The efficacy of the CDK18 knockdown was evaluated by Western blot analysis. CDK18 and as a loading control Pan-cadherin were detected. Signals were quantified by densitometric analysis. Statistical analysis was performed using the unpaired t-test, significant differences are indicated, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01. Mean ± SEM are plotted, n = 3–6 independent experiments per condition.