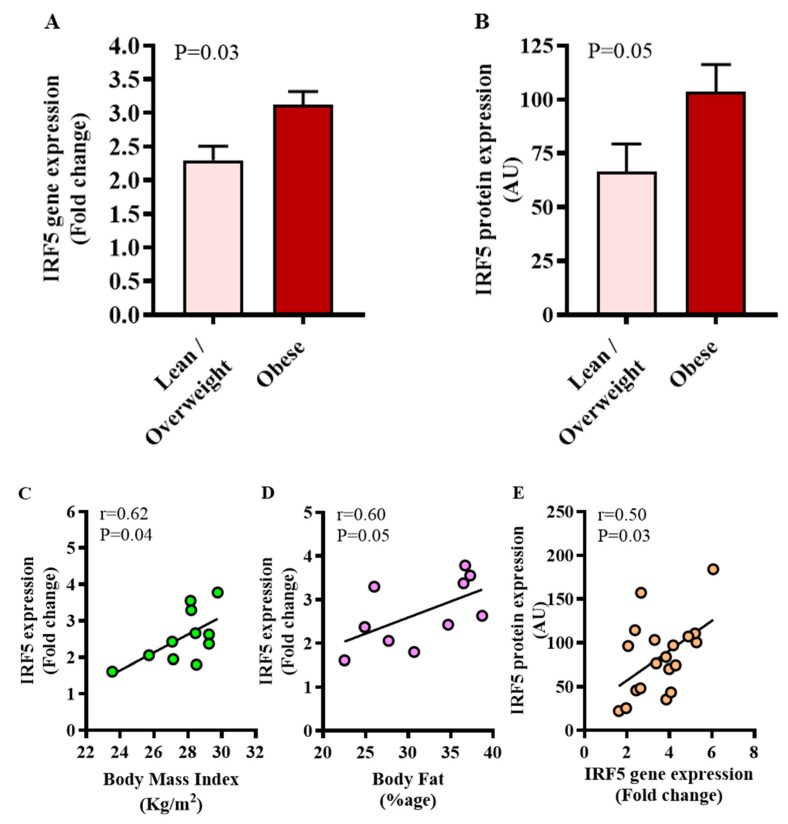
Figure 1.
Increased adipose tissue interferon regulatory factor (IRF)5 expression in diabetic obese patients. IRF5 gene expression was assessed in the adipose tissue by using qRT-PCR in 46 type-2 diabetic (T2D) patients and expression of the IRF5 protein was determined by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in 19 T2D patients as described in materials and methods. Regarding qRT-PCR, GAPDH gene expression was used as internal control. The expression level of IRF5 gene relative to control (lean adipose tissue) was calculated by using 2−ΔΔCt method and expressed as relative mRNA expression or fold change over the average control expression taken as 1. Regarding IHC, IRF5 protein staining intensity, expressed as arbitrary units (AU), was determined by using Aperio-positive pixel count algorithm and ImageScope software. The number of positive pixels was normalized to total pixels (positive and negative) and color/intensity thresholds were set with immunostaining as positive and background as negative pixels. The data (mean±SEM) show significantly elevated (A) IRF5 gene expression (fold change) (p = 0.03) and (B) IRF5 protein expression (AU) (p = 0.05) in diabetic obese compared to diabetic lean/overweight patients. Furthermore, in diabetic lean/overweight subjects (11), IRF5 gene expression was found to associate positively with (C) body mass index (BMI: r = 0.62, p = 0.04) and (D) %age of body fat (r = 0.60, p = 0.05). (E) Overall, IRF5 gene and protein expression were found to be mutually concordant (r = 0.50, p = 0.03).