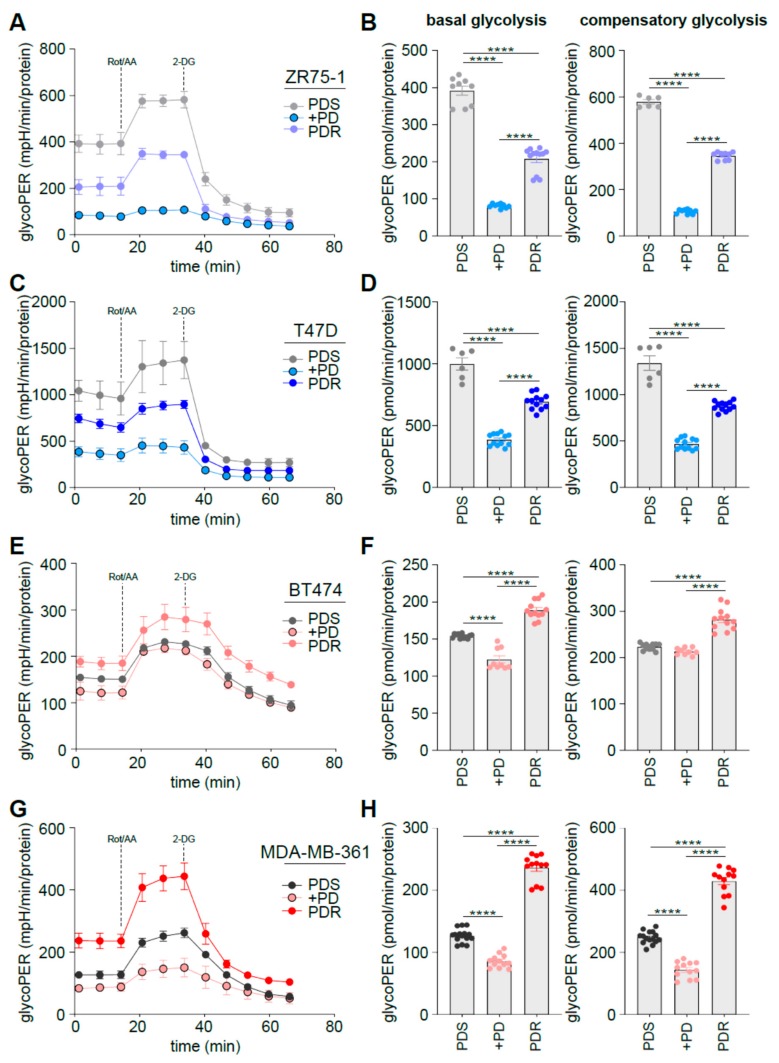
Figure 3.
HER2 status impacts on glucose catabolism and reveals different glucose dependency during acute and chronic palbociclib administration. (A, C, E, G) PDS (either in presence or absence of 1 µM palbociclib, PD) and PDR cells were subjected to seahorse XFe96 glycolytic rate analysis and glycolytic proton efflux rate (glycoPER)) was measured in real time and normalized on protein levels. (B, D, F, H) Basal and compensatory (i.e., when electron transport chain is impaired) glycolytic capacity was calculated as described in Method Details, based on the extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) and oxygen consumption rate (OCR) after the administration of the respiratory complex I inhibitor rotenone, together with the respiratory complex III inhibitor antimycin A following by the glycolysis inhibitor 2-deoxy-glucose (2-DG). Data represent means ± SEMs. Each dot represents at least three technical replicates from three biological replicates. Blue dots are from HER2− cells, red from HER2+. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s corrected; **** p < 0.0001.