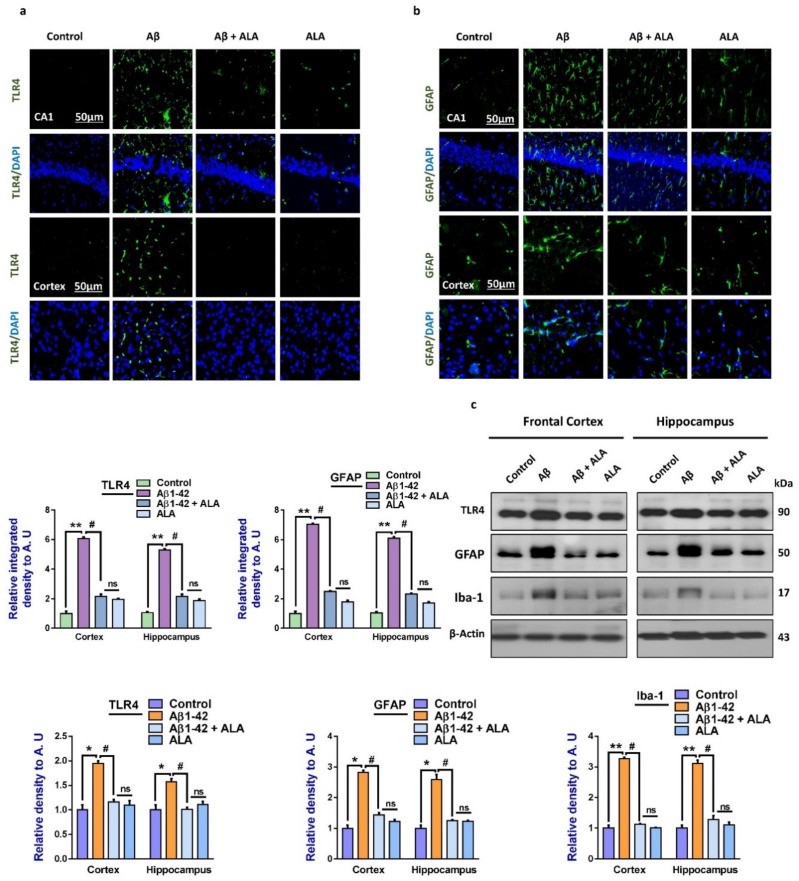
Figure 1.
Effects of alpha linoleic acid against amyloid-beta (Aβ)-induced activated Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and ionized calcium adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1) in mouse brains. (a) and (b): Immunofluorescence results of TLR4 and GFAP in the frontal cortices and hippocampi (CA1) of the treated mice groups, with respective bar graphs. Magnification: 30×; scale bar: 30 and 50 µm. (c) Western blot results of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), glial fibrillary acidic proteins (GFAP), and ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1), with respective bar graphs. * Significantly different from the Aβ-treated group; # significantly different from the Aβ + ALA-cotreated group. Significance = * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; # p < 0.05; and ## p < 0.01. Aβ: amyloid beta; ALA: alpha linoleic acid; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; ns = non significant.