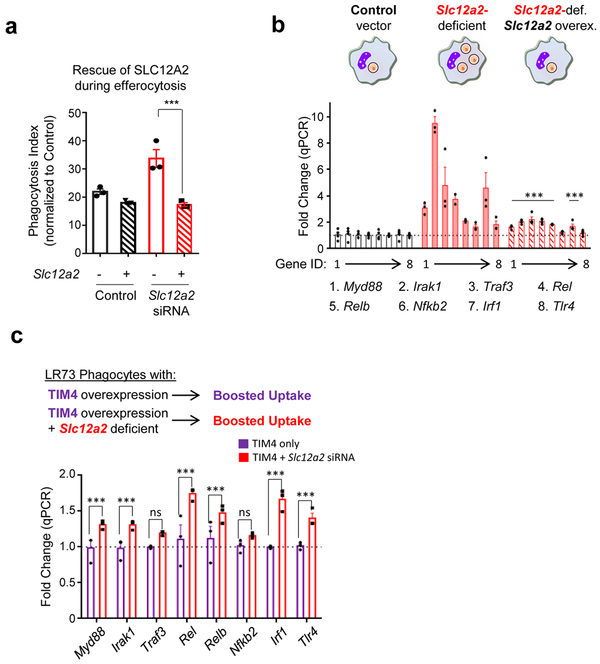
Extended Data Fig. 3. SLC12A2 deficiency overrides homeostatic efferocytosis signature.
(a and b) Overexpression of SLC12A2 restores appetite suppression and reverses the pro-inflammatory gene signature in engulfing Slc12a2-deficient phagocytes. A control vector or Slc12a2 cDNA was overexpressed in control or Slc12a2-deficient LR73 phagocytes. Phagocytes were then mixed with CypHer5E-labeled apoptotic Jurkat cells for 2 h, cDNA+ CypHer5E+ phagocytes were sorted (a) and assessed for the presence of a pro-inflammatory gene signature by qPCR (b). Data represent n=3 independent experiments. Data shown as mean ± SEM. ns = not significant, ***p < .001.
(c) Slc12a2 knockdown induces pro-inflammatory genes in normally anti-inflammatory efferocytosis after TIM-4 overexpression. TIM4 stably expressing LR73 phagocytes were transfected with control siRNA or Slc12a2 siRNA, and then co-cultured with apoptotic cells for 2 h. RNA was subsequently isolated from the phagocytes, and the pro-inflammatory gene signature was assessed via qPCR. Data represent n=3 independent experiments. Data shown as mean ± SEM. ns = not significant, ***p < .001. Statistics source data are provided in Source Data Extended Data Figure 3.