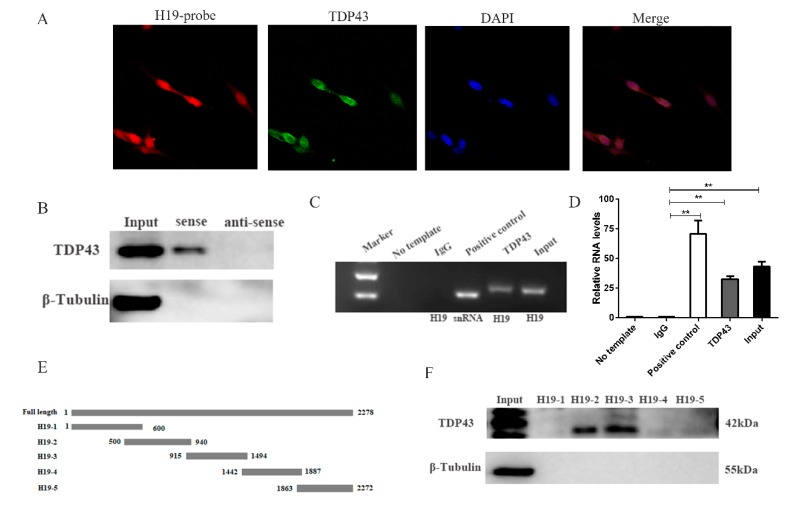
Figure 1.
H19 physically interacts with TDP43. (A) Confocal Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH) images of co-localization of H19 and TDP43. (B) Biotin-labeled full-length H19 was used to pull down TDP43 protein. Western blotting analysis was performed to detect the TDP43 protein. β-Tubulin was used as negative control. (C) RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays were performed to validate the interaction between H19 and TDP43. SNRNP70 was used as positive control. The H19 and snRNA transcripts were assessed by PCR. (D) qPCR result of RIP assay. (E) The location of the H19 mutant fragments. (F) The interactions between a series of H19 mutant fragments (H19-1, H19-2, H19-3, H19-4, H19-5) were assessed by RNA pull-down assays. Mean values ± SD, n = 3. * means p < 0.05, ** means p < 0.01.