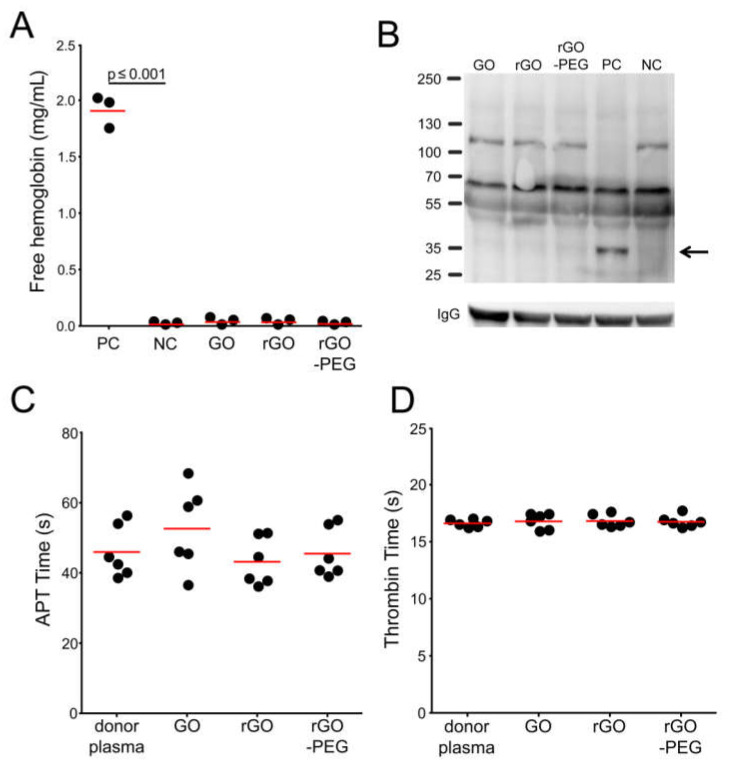
Figure 2.
Hemocompatibility of GO, rGO, and rGO-PEG: (A) Detection of hemolysis in the presence of graphene derivatives at 50 µg/mL with normal healthy donor (NHD) venous blood. Positive (blood in PBS + 1% Triton X-100) and negative (blood in PBS) controls were employed. Each dot represents a mean value of one donor. One-way analysis of variances with Tukey’s multiple comparison test was used. (B) Determination of the activation of the complement system in fresh human plasma co-incubated with 50 µg/mL of graphene derivatives. Positive (plasma + Cobra venom factor (CVF); PC) and negative (plasma + PBS; NC) controls were employed. The complement activation product is depicted by a black arrow. C3 (α chain) is 115 kDa; C3 split products are around 43 kDa. The molecular weight marker is shown on the left. The image is representative of three independent experiments. Measurement of plasma coagulation time: Fresh human plasma was co-incubated with 50 µg/mL of graphene derivatives for 30 min at 37 °C. Plasma coagulation was induced by the addition of calcium chloride and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) reagent or thrombin, and aPTT (C) or thrombin time (D) were recorded, respectively. One-way analysis of variances with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test was applied. Technical duplicates were used, n = GO, graphene oxide; rGO reduced graphene oxide; rGO-PEG, PEGylated reduced graphene oxide; CVF, cobra venom factor; aPTT, activated partial thromboplastin time.