Figure 2.
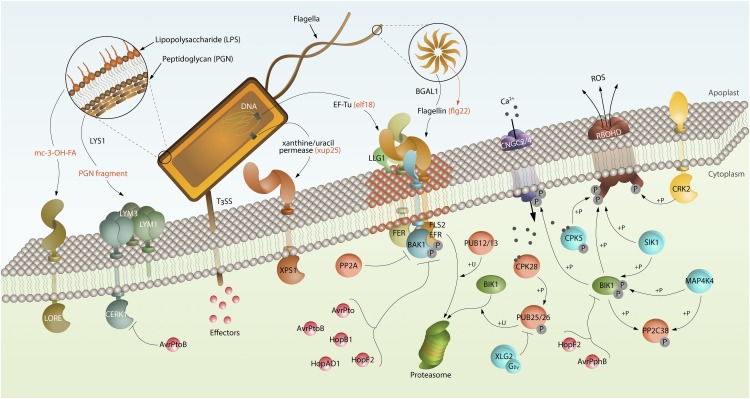
Interactions between the bacterial pathogen P. syringae and Arabidopsis surface sensor systems. Arabidopsis employs several plasma membrane immune receptors that detect multiple patterns derived from P. syringae. These include LORE, which perceives mc-3-OH-FA; the CERK1–LYM1–LYM3 complex, which perceives PGN fragments released by LYS1; XPS1, which perceives xanthine/uracil permease (xup25); EFR, which perceives EF-Tu (elf18); and FLS2, which perceives flagellin (flg22) and is deglycosylated by BGAL1. FER and LLG1 associate with FLS2/EFR and regulate immune complexes, which may reside in specific plasma membrane nanodomains (rust-colored). BIK1 plays a central role in early responses after PAMP recognition. Upon flg22 perception, BAK1 associates with and transphosphorylates FLS2, leading to BIK1 activation and disassociation from FLS2–BAK1 complex. Activated BIK1 phosphorylates CNGC2/4 and RBOHD to regulate Ca2+ influx and ROS production, respectively. CPK5 and SIK1 also phosphorylate RBOHD, and SIK1 and MAP4K4 phosphorylate and stabilize BIK1 to ensure robust ROS production. BIK1 function is negatively regulated by PP2C38 in the resting state, whereas PP2C38 is phosphorylated by BIK1 and MAP4K4 and is released from BIK1 upon flg22 perception. To tightly control the immune responses, BAK1 is negatively regulated by PP2A. FLS2 and nonphosphorylated BIK1 are polyubiquitinated by E3 ligases PUB12/13 and PUB25/26, respectively, targeting them for degradation. Furthermore, heterotrimeric G-protein (XLG2/Gβ/Gγ) stabilizes BIK1 by inhibiting PUB25/26 activity in the resting state. Upon flg22 perception, the heterotrimeric G-protein disassociates from FLS2–BIK1 complex. CPK28 is further activated to phosphorylate PUB25/26 to accelerate nonphosphorylated BIK1 degradation, which in turn allows the phosphorylated BIK1 to activate downstream signaling. To suppress plant immune responses, P. syringae transports effectors (eg. AvrPto, AvrPtoB, HopB1, HopAO1, HopF2) through a type-III secretion system (T3SS) to inhibit the functions of receptor complex (e.g. FLS2, EFR, BAK1, and CERK1) and other key signaling components (e.g. BIK1).