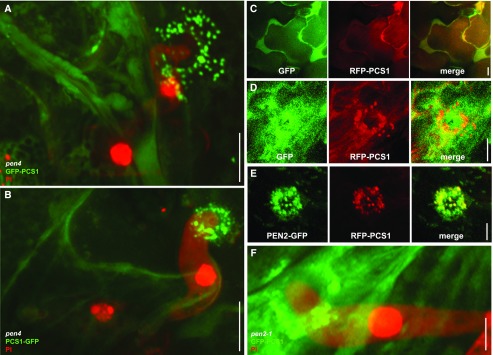
Figure 2.
Pathogen attack triggers translocation of cytoplasmic PCS1 and mitochondrial colocalization with PEN2 at fungal penetration sites. Three-week-old Arabidopsis seedlings were inoculated with the nonadapted powdery mildew Bgh. The epidermis of the first true leaves was visualized by confocal laser scanning microscopy 12–16 h after Bgh inoculation. The fungal structures are stained with propidium iodide except in GFP/RFP localization experiments. All pictures represent the average Z-projection of stacks of 30–50 sections, except in the case of C, where a single median section is shown. A and B, Localization at the attempted penetration site of GFP-PCS1 (A) or PCS1-GFP (B) in a pen4 mutant leaf epidermal cell. C Cytosolic localization of soluble GFP with RFP-PCS1 in noninfected epidermal cells. D, Translocation of RFP-PCS1, but not soluble GFP, into aggregates at the penetration site. E, Colocalization of RFP-PCS1 with mitochondria-associated PEN2-GFP at the penetration site. F, Localization of GFP-PCS1 in a pen2 mutant background after Bgh infection. Scale bars = 10 μm (A–C) or 5 μm (D–F).