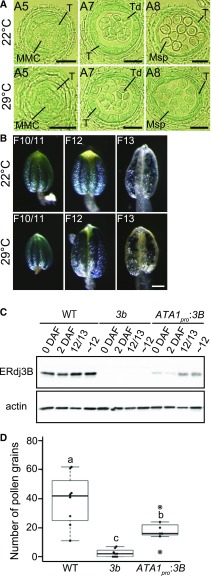
Figure 4.
Expression of ERDJ3B in tapetum cells. A, Semithin sections of GUS-stained anthers at various stages of development from transformants grown at 22°C (top row) or 29°C (bottom row), observed using differential interference contrast microscopy. Anthers at anther stage 5 (A5), anther stage 7 (A7), and anther stage 8 (A8) are shown. MMC, Microspore mother cells; Msp, microspores; T, tapetum cell; Td, tetrads. Bars = 20 μm. B, The expression patterns of anthers at flower stage 10/11 (F10/11), flower stage 12 (F12), and flower stage 13 (F13) in transformants expressing the GUS gene driven by the ERDJ3B promoter grown at 22°C (top row) or 29°C (bottom row). Bar = 100 μm. C, Immunoblots of total proteins extracted from samples collected 0 d after flowering (0 DAF) and 2 DAF, from flower buds at flower stages 12 and 13 (12/13), and from flower buds prior to flower stage 12 (∼12) from the wild type (WT), erdj3b-1 [3b], and erdj3b-1 harboring the ATA1pro:3B transgene [ATA1pro:3B] grown at 22°C. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-ERdj3B and anti-actin antibodies. D, Number of pollen grains on stigmas of the wild type, erdj3b-1, and erdj3b-1 harboring the ATA1pro:3B transgene; plants were grown at 29°C (n = 8, 8, and 7, respectively). Dots represent the number of pollen grains on each stigma; circles indicate outliers. Statistical differences were calculated using the Tukey-Kramer method. P < 0.05 is indicated by different letters.