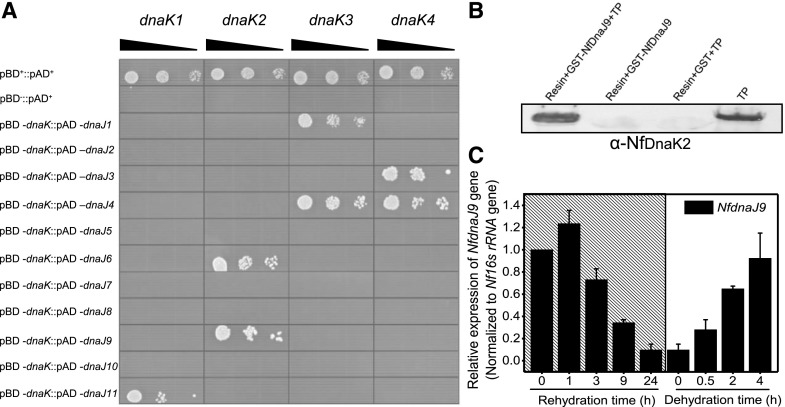
Figure 3.
Interaction of NfDnaK and NfDnaJ in N. flagelliforme, and the relative transcriptional levels of NfdnaJ9 during rehydration and subsequent dehydration. A, In vitro protein-protein interaction analyses of NfDnaK and NfDnaJ by Y2H assay. The yeast transformants (10 μL each of cell suspensions diluted from OD600 0.1 to 0.001, as indicated by the slope of the black triangles from left to right) expressing positive control plasmids (pAD+ and pBD+), negative control plasmids (pAD+ and pBD−), and plasmids for testing protein interaction (pAD-NfdnaJ and pBD-NfdnaK) were grown on SD/-Trp-Leu-His-Ade agar plates for 3 d. B, In vivo pull-down analysis of the interaction between NfDnaK2 and NfDnaJ9. The total proteins (TP) extracted from dried field N. flagelliforme samples were incubated with GST-binding resin and GST-tagged NfDnaJ9 (Resin+GST-NfDnaJ9+TP), and the coeluted products were detected with the specific antibody against NfDnaK2. The eluted products of the incubation mixture of resin and GST-tagged NfDnaJ9 (Resin+GST-NfDnaJ9),or resin, GST, and TP (Resin+GST+TP) were used as negative controls to exclude nonspecific interference, and TP extraction was used as the positive control. C, Relative transcriptional levels of NfdnaJ9 during rehydration and subsequent dehydration. The dried field-collected N. flagelliforme samples were rehydrated (hatch marks) for 0, 1, 3, 9, and 24 h and subsequently dehydrated for 0.5, 2, and 4 h. Each treatment was repeated three times independently, and data are shown as the mean ± sd of three independent replicates.