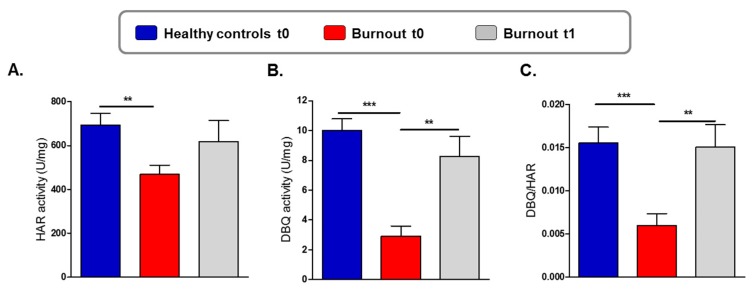
Figure 2.
Reduced complex I content and activity in mitochondria from individuals with burnout and impact of physical activity. (A) Reduced complex I content as revealed by a significant reduction of NADH:HAR activity («HAR activity») in the group with burnout compared to healthy controls at baseline (t0). Student’s t test ** p = 0.0036. (B) Reduced “genuine” complex I activity as revealed by a significant reduction of NADH-ubiquinoneoxidoreductase (NADH:DBQ) activity («decylubiquinone (DBQ) activity) in the group with burnout compared to healthy controls at baseline (t0). Physical activity significantly increased DBQ activity in the burnout group at study end (t1). Student’s t test ** p = 0.0017, *** p < 0.0001. (C) The DBQ/HAR ratio was determined via normalization of complex I activity to the complex I content of the mitochondrial protein preparation. A significantly reduced DBQ/HAR ratio in individuals with burnout compared to healthy controls indicates a “functional” reduction of complex I activity at baseline (t0). Physical exercise improved significantly complex I activity in the burnout group. Student’s t test ** p = 0.0053, *** p = 0.0004. Values are represented by the mean ± SEM.