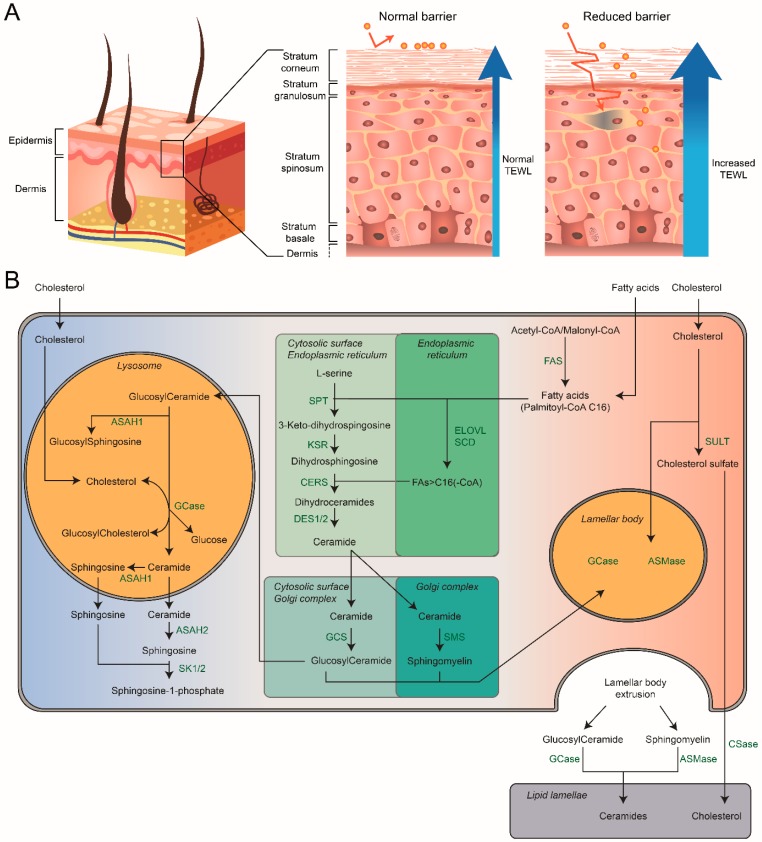
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the human skin and the main processes involved around GCase and its related lipids. (A) Schematic overview of a cross section of the skin showing the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue. The middle illustration shows a more detailed view of the epidermis under healthy conditions. The right illustration depicts a more detailed view of the epidermis with a reduced barrier. Exogenous compounds can get into deeper layers of the epidermis when the barrier is reduced, resulting in an immune response. It also leads to an increased transepidermal water loss (TEWL). (B) Schematic overview of the main processes involved around GCase within the cell. Arrows indicate the transport or conversion of lipids; associated enzymes are listed adjacent to their abbreviations. ASAH1: acid ceramidase, ASAH2: neutral ceramidase, ASMase: acid sphingomyelinase, CERS: ceramide synthase family, CSase: cholesterol sulfatase, DES1/2: dihydroceramide desaturase 1 and 2, ELOVL: elongation of very long chain fatty acids family, FAS: fatty acid synthase, GCase: β-glucocerebrosidase, GCS: glucosylceramide synthase, KSR: 3-ketosphinganine reductase, PLA-2: phospholipase, SCD: stearoyl-CoA desaturase, SMS: sphingomyelin synthase, SPT: serine palmitoyltransferase, SULT: cholesterol sulfotransferase type 2 isoform 1b.