Fig. 1.
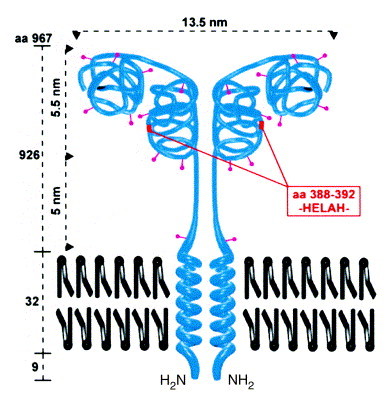
Structure of CD13. The type II membrane protein is found as a dimer of two non-covalently associated subunits with a relative molecular mass of 160 kDa each. CD13 has ten N-glycosylation sites (∼400 carbohydrate residues comprising approximately 40% of the molecular mass). Analogous to aminopeptidase A (APA)71, a two-domain structure can be hypothesized with a substrate-binding site in the C-terminal and the active center in the N-terminal domain. The dimensions of the molecule are taken from Noren et al.11
