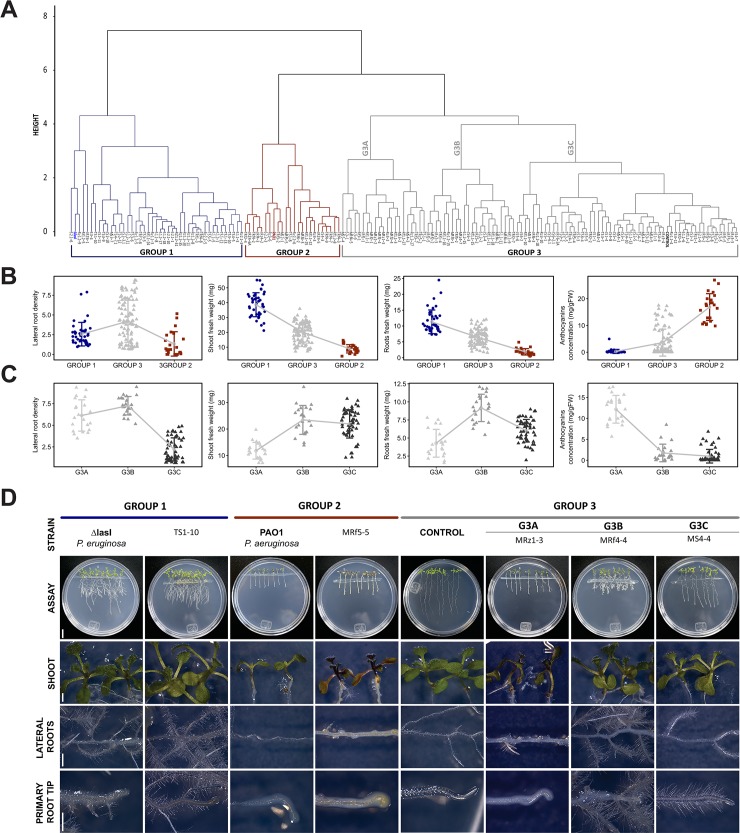
Fig 1. Avocado rhizosphere bacteria with plant growth-promoting activity in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Cluster analysis of bacterial isolates associated with Persea americana Miller evaluated in the Arabidopsis-bacteria coculture system, ANOSIM, p<0.05, R = 0.67. (A) Dendrogram resulting from the cluster analysis of the 162 selected isolates. (B) Analysis of the grouping pattern of Groups 1, 2 and 3 considering the arithmetic means per group for each variable. (C) Grouping patterns of subgroups G3A, G3B, and G3C. The points represent each of the observations, and the bars represent the standard deviation. (D) Representative images of the growth of Arabidopsis seedlings inoculated with strains associated with the different groups and subgroups. Control plants are shown as uninoculated or inoculated with P. aeruginosa PAO1 (wild-type strain, pathogenic) and P. aeruginosa ΔlasI (QS mutant strain, promoter). Scale bar: Petri dishes = 1 cm; plant zones = 3 mm.