FIG. 5.
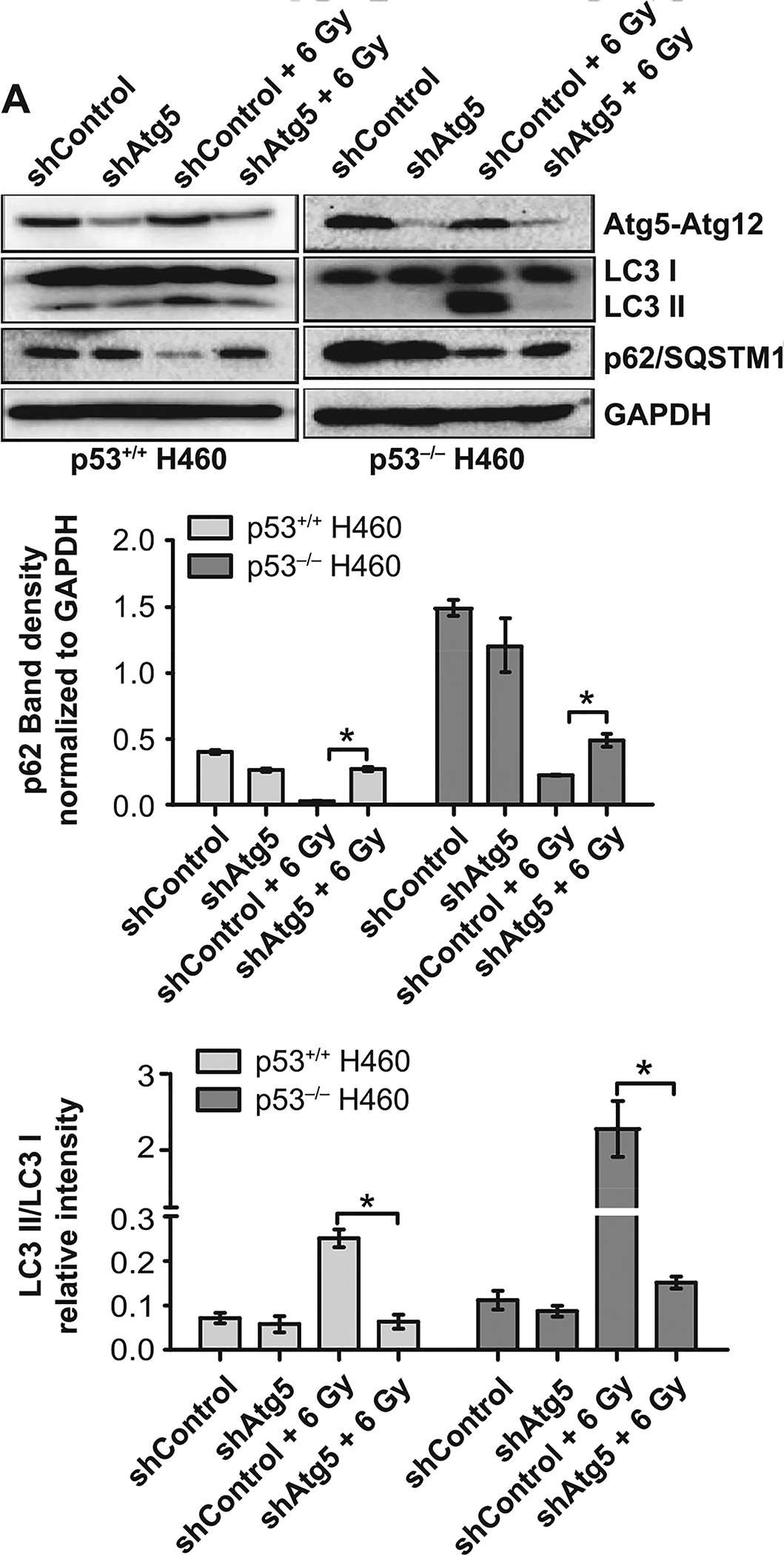
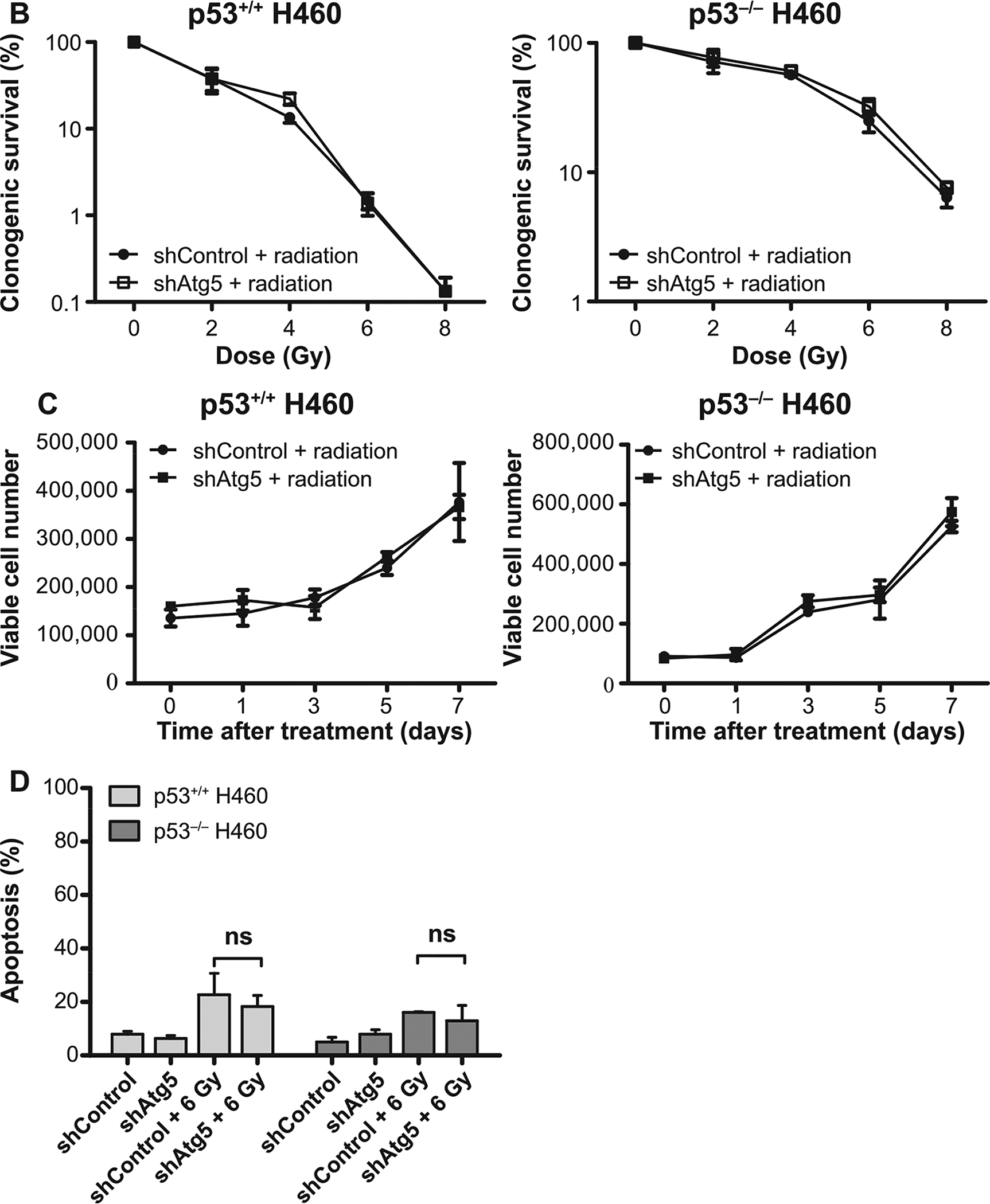
Atg5 knockdown fails to alter radiation sensitivity in H460wt or H460crp53 cells. Panel A: ATG5 knockdown. Cells were collected 3 days postirradiation. Western blot showing ATG5 knockdown in H460wt and H460crp53 cell lines; inhibition of autophagy in shAtg5 H460wt and shAtg5 H460crp53 cell lines is indicated by reduced conversion of LC3 I to LC3 II and interference with degradation of p62/SQSTM1. The bar graph in each panel indicates the relative band intensity generated from densitometric scans of two independent experiments in arbitrary densitometric units. Panel B: Lack of radiation sensitization by autophagy inhibition. Clonogenic survival assay showing that Atg5 knockdown has no effect on radiosensitivity in either cell line. Cells were irradiated at the indicated doses and incubated for 11 days prior to assessment of colony formation. Panel C: Lack of radiation sensitization by autophagy inhibition. Temporal viability assay indicating that Atg5 knockdown has no effect on radiosensitivity in both H460wt and H460crp53 cells. Cells were 6 Gy irradiated. Panel D: Autophagy inhibition does not increase the extent of radiation-induced apoptosis. Annexin V/PI staining indicating that radiation-induced apoptosis was unaltered after Atg5 knockdown in both H460wt and H460crp53 cell lines. Unless stated otherwise, data are from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, irradiated shControl cells vs. irradiated shAtg5 cells.
