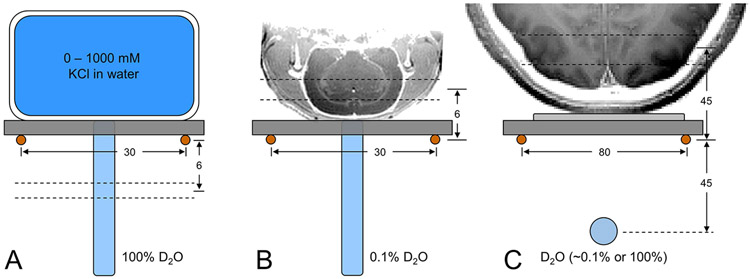
Figure 1:
Experimental setups to characterize DMI (A) on phantoms in vitro, (B) on rat brain post mortem and (C) on human brain in vivo. Due to the lack of a 1H MRI coil, all images were acquired in a separate study and are shown for illustration purposes only. (A) Phantoms with (R3.9) different KCl concentrations are used to change sample conductivity, and hence achieve a range of coil loads in vitro, whereby signal is always acquired from a 2 mm slice 6 mm below the 2H RF coil. (B, C) On rat brain post mortem and human brain in vivo, signal is acquired in the form of 3D DMI whereby analysis is limited to the indicated slice position. On human brain a 100% D2O phantom was used for RF power calibration and then replaced with a 0.1% D2O phantom for position referencing during DMI. All distances are in mm.