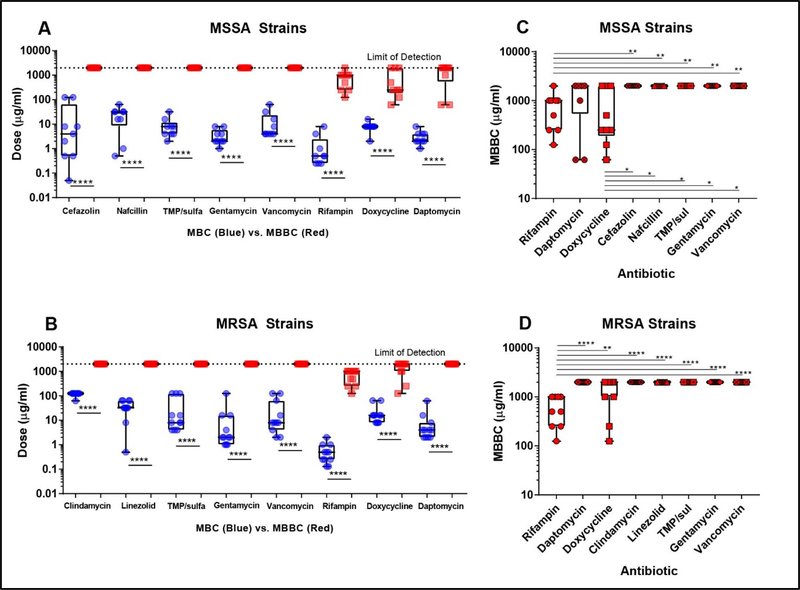
Figure 3. Clinically important antibiotics are unable to effectively kill MSSA and MRSA S. aureus biofilms.
S. aureus planktonic minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) was compared to minimum biofilm bactericidal concentration (MBBC) for MSSA (A) and MRSA (B). All clinical and laboratory strains show increased tolerance to all antibiotics tested in our panel with MBBC values all statistically significantly higher (p<0.0001****) than the MBC values (A-B). In MSSA isolate biofilms, the rifampin and doxycycline treatment groups had a significantly lower MBC (p<0.05 *, p<0.0001 ****) compared to the remaining antibiotics (C). In MRSA isolate biofilms, only the rifampin treatment group had significantly lower MBC (p<0.0001 ****) compared to remaining antibiotics (D).