Figure 11.
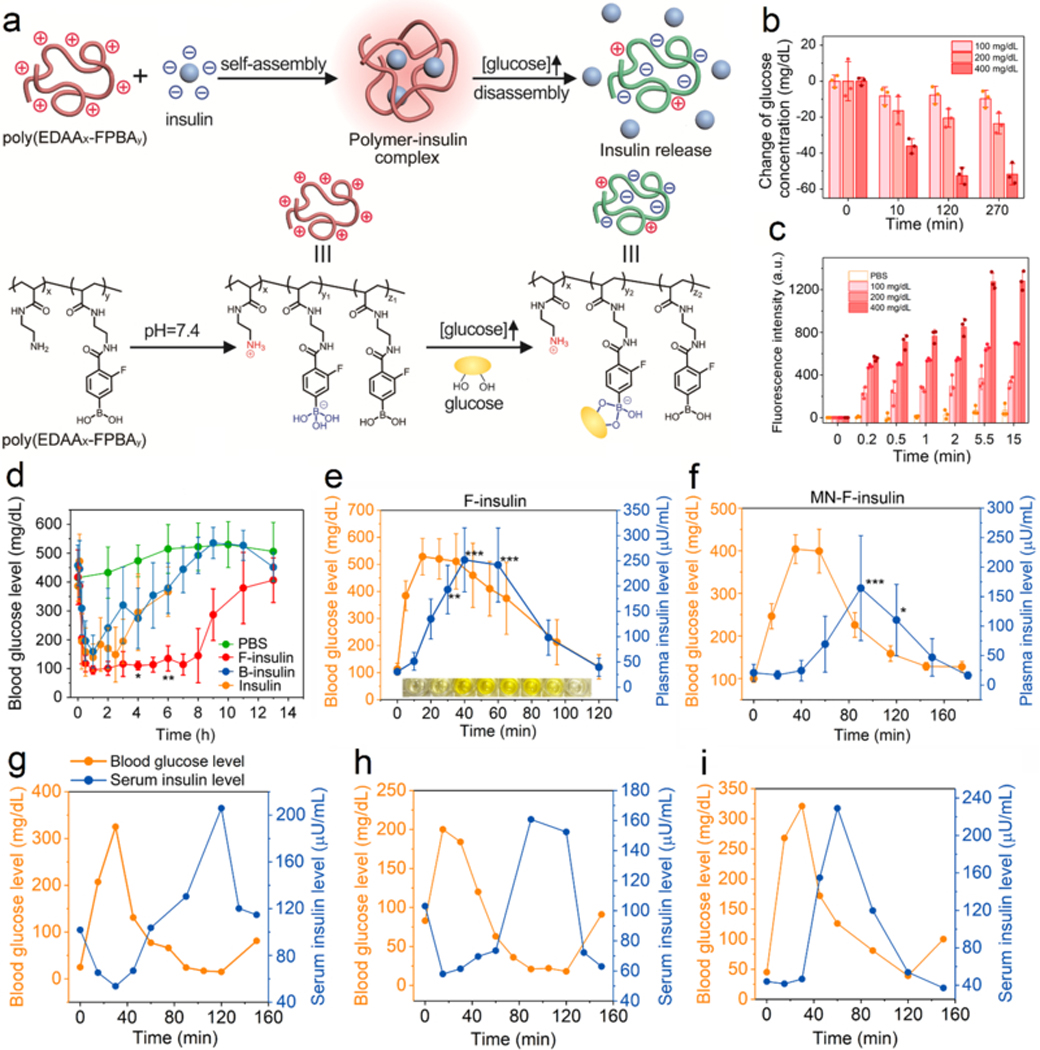
Glucose-responsive insulin release from the complex prepared from insulin and a charge-reversal cationic polymer. (a) Schematic of glucose-triggered charge-reversal and subsequent insulin release. (b) Glucose-binding ability of polymer. (c) Glucose-triggered insulin release. (d) Blood glucose regulation ability of the prepared complex in a type 1 diabetic mouse model. n=5. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (e) Diabetic mice receiving treatment were further administrated with glucose. Both blood glucose levels and plasma insulin levels were monitored. n=4 to 5. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (f) Diabetic mice receiving treatment of microneedle patches loaded with complex were further administrated with glucose. Both blood glucose levels and plasma insulin levels were monitored. n=4. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (g-i) Diabetic minipigs receiving complex treatment were administrated with dextrose solution intravenously. Both blood glucose levels and serum insulin levels were measured. Each Figure indicated one diabetic minipig. Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2017, AAAS.
