Figure 5. A simplified schematic diagram showing the key pathways for autophosphorylation at the activating and inhibitory sites, in the absence or presence of Ca2+/CaM.
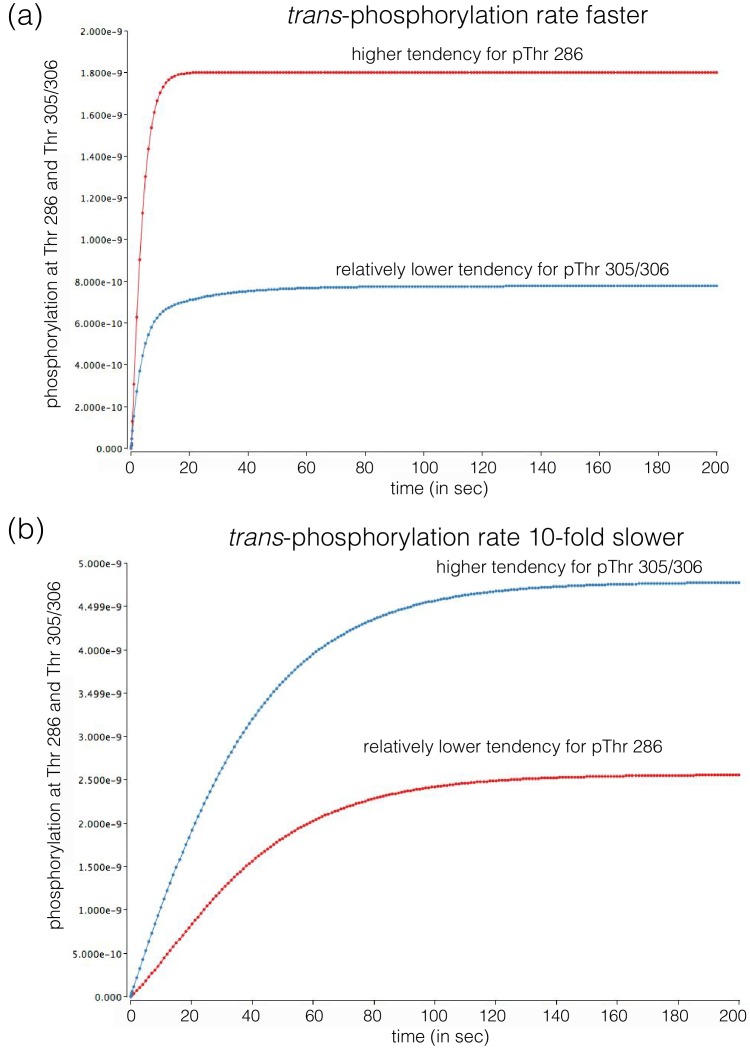
While Thr 305/306 can get phosphorylated both in cis in the absence of Ca2+/CaM or in trans in the presence of Ca2+/CaM, autophosphorylation of Thr 286 can only happen in trans in the presence of Ca2+/CaM. Ca2+/CaM shows a rapid association and dissociation until CaMKII gets phosphorylated at Thr 286, when its affinity for Ca2+/CaM increases by about 1000-fold. A detailed description of all the different reactions and conditions that form the basis of our kinetic model is provided in the Appendix.