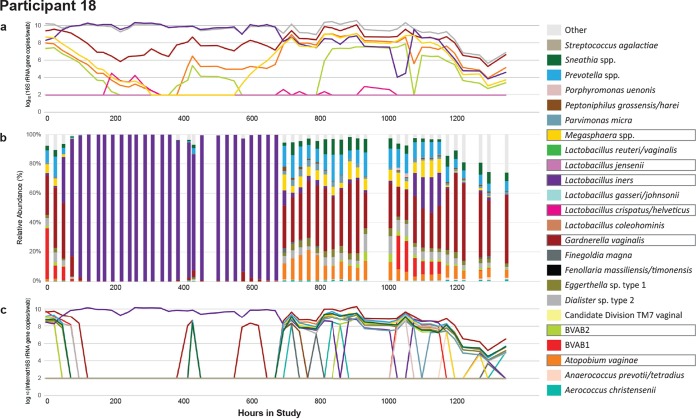
FIG 1.
Complex bacterial kinetics in the vaginal niche in a representative study participant. Daily samples from a woman, participant 18, who performed self-swabbing of the vagina were analyzed by targeted qPCR of seven specific species (a), high-throughput sequencing using 16S rRNA (b), and inferred concentration for species with a relative abundance above 1% (c). Boxes around taxa indicate they were measured using qPCR. qPCR allows measures of the absolute concentration, whereas broad-range PCR with sequencing provides a measure of the bacterial diversity in a given sample. Targeted qPCR often detects shifts in single species prior to NGS. Inferred concentration follows qPCR more closely than does the relative abundance and may project the concentration of species for which targeted qPCR assays are not available. Traces for the remaining participants can be found in Fig. S1.