Figure 6. CHIKV E1-V80 mutational network.
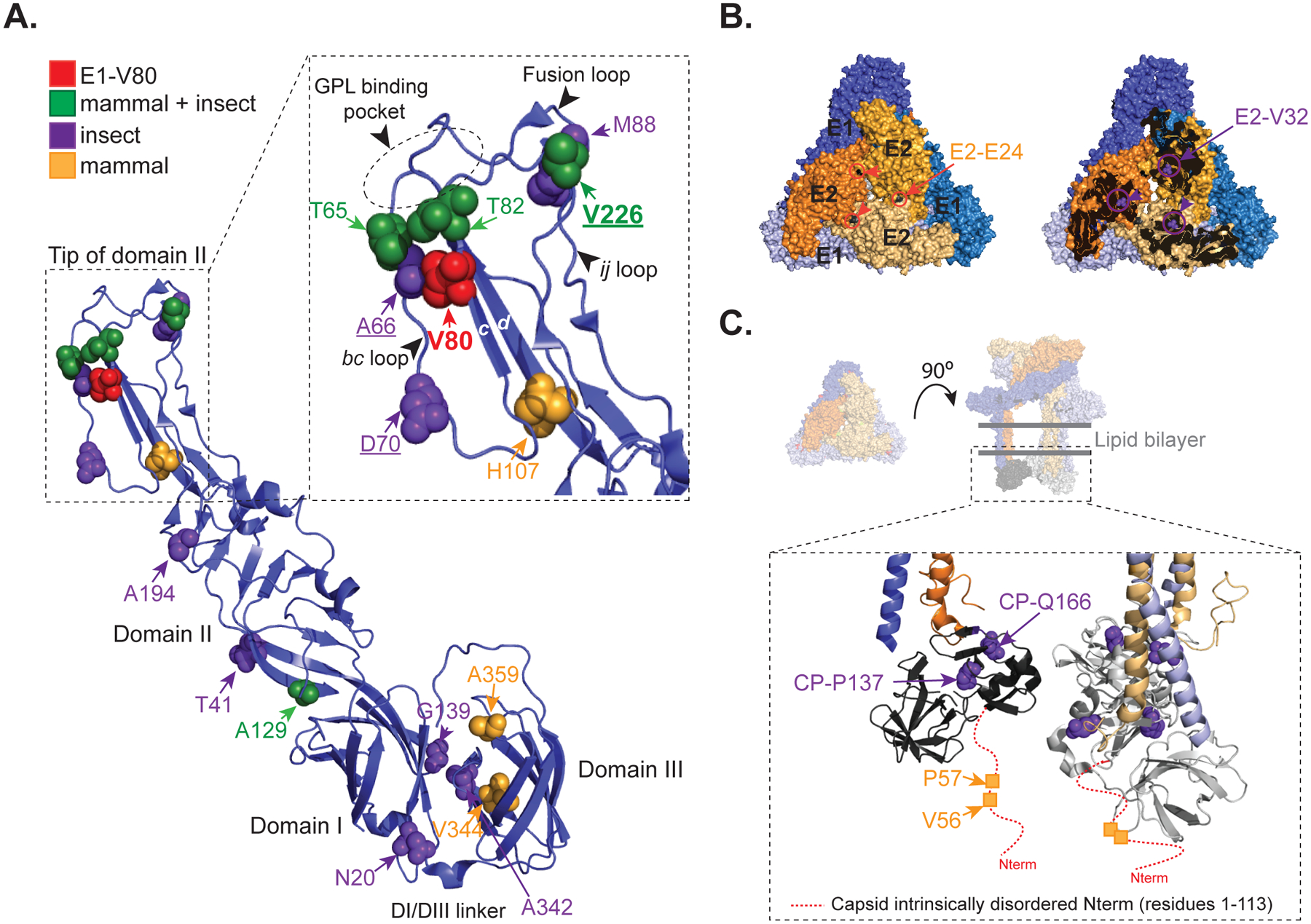
(A) Ribbon representation of the CHIKV E1 glycoprotein (PDBID: 3N42). Second-site mutations found only in mammalian, mosquitoes or both mammalian and mosquito experiments are represented as orange, purple and green spheres, respectively. Detail of the tip of domain II (residues 53–108 and 218–235) is shown in the inset. Residue E1–80 is highlighted in red. Residues E1–226, E1–66 and E1–70, previously described as cholesterol-dependent mutants are underlined. Fusion loop, ij loop, bc-loop, β-strand c, β-strand d, and the GPL binding pocket are indicated. (B) Representation of a single trimeric spike showing position E2–E24 (black spheres) and E2-V32 (green spheres) are indicated (PDBID: 3J2W). E1 (blue) and E2 (orange) glycoproteins from different heterodimers are depicted in different color intensities for clarity. (C) Schematic representation of a single trimeric spike with the transmembrane domains and the capsid protein (PDBID: 3J2W). In the inset is shown the globular domains of the capsid protein (residues 113 to 261). The red dashed-line indicates the intrinsically disordered domain from the capsid protein absent in the crystal structure (residues 1 to 113). For clarity the mutations are depicted in only one monomer.
