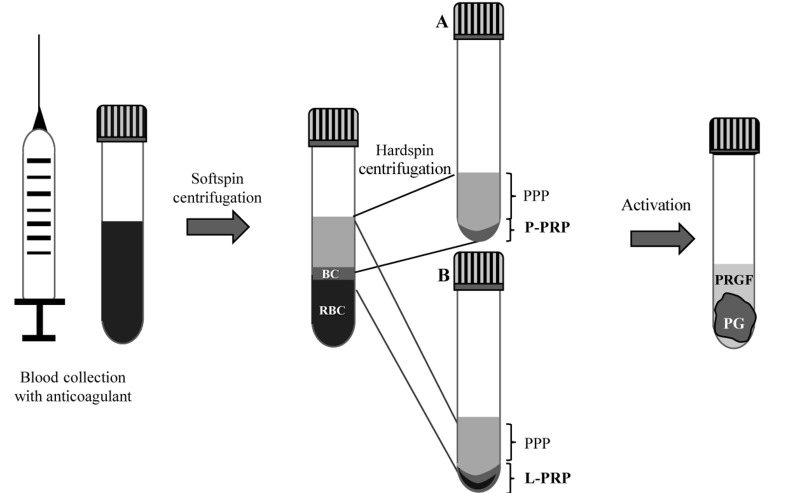
Figure 1.
Two-step centrifugation protocol to obtain pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP), leucocyte- and platelet-rich plasma (L-PRP), platelet gel (PG) and plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF)
The first step consists of “softspin” centrifugation of the whole blood that leads to three layers: an upper layer containing mostly platelets and white blood cells, an intermediate “buffy coat” (BC) layer rich in white blood cells and a bottom layer consisting mostly of red blood cells (RBC). To produce the P-PRP the upper layer and superficial BC are transferred to a new tube and “hardspin”-centrifuged to obtain P-PRP at the bottom of the tube and platelet-poor plasma (PPP) on the top (A). To obtain L-PRP, instead, the upper layer and the whole BC along with some RBC are transferred to a new tube and “hard spin”-centrifuged to obtain L-PRP at the bottom of the tube and PPP at the top (B). The PPP is removed and P-PRP or L-PRP eventually activated to induce clotting and produce the PG and PRGF. Fibrin glue (FG) is obtained from coagulation of PPP17,23,25.