FIGURE 3.
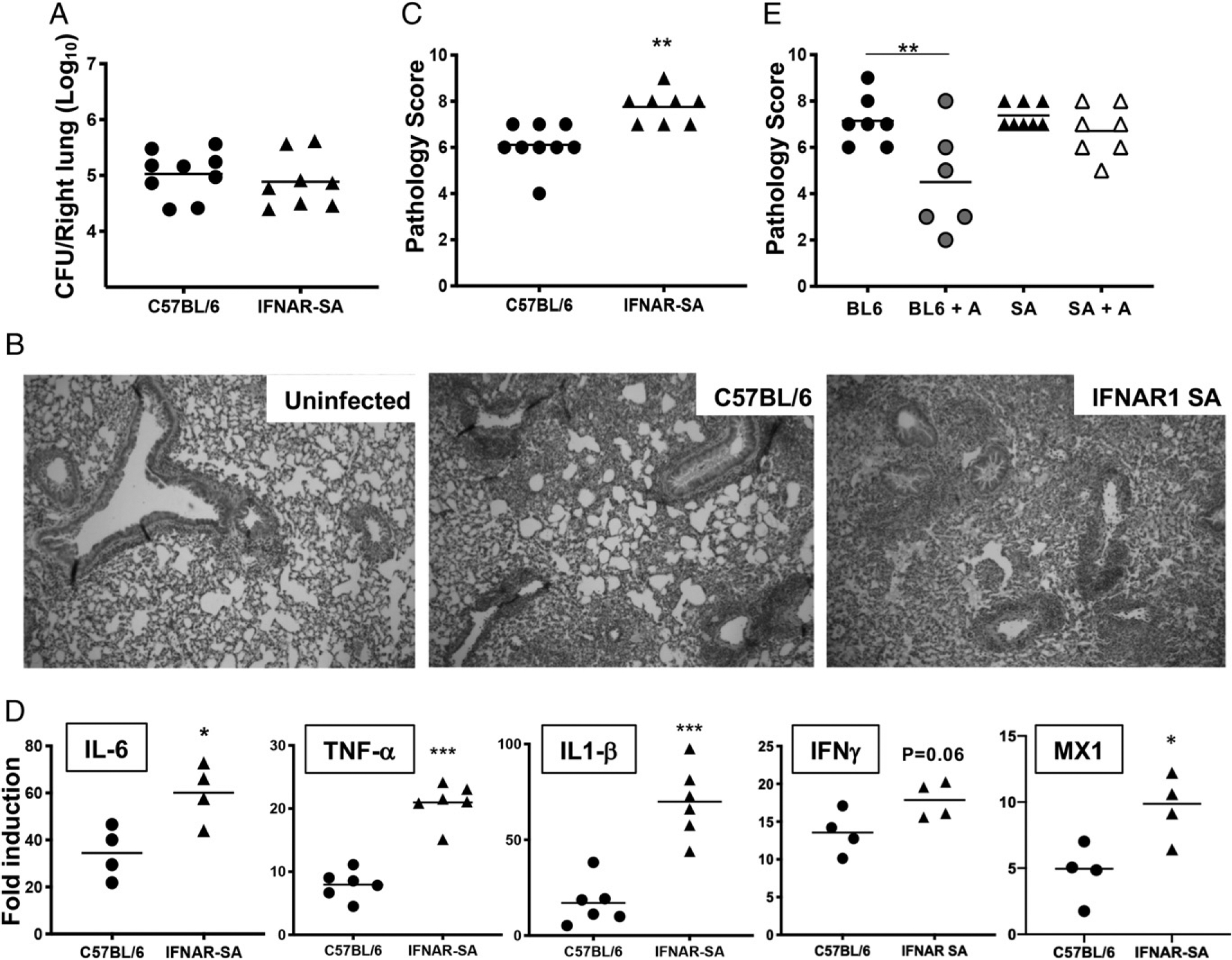
Increased IFNAR1 signaling leads to exacerbated lung inflammation in B. pertussis–infected adult mice. C57BL/6 or IFNAR-SA mice (n ≥ 4 per group) were euthanized on day 7 postinoculation with B. pertussis or PBS sham inoculum, and lungs were dissected for assessment of outcomes. (A) Bacterial burdens. (B) Representative H&E-stained inflammatory pathology images (original magnification 340) of uninfected and infected C57BL/6 and infected IFNAR1-SA mouse lung sections. (C) Inflammatory pathology scores assessed from lung histology sections. (D) Fold induction (infected versus sham inoculated) of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN-γ, and MX1 mRNA levels. (E) Infected C57BL/6 (BL6) or IFNAR1-SA (SA) mice (n ≥ 6 per group) were treated with AAL-R (+A) or PBS intranasally 24 h postinoculation and euthanized on day 7 postinoculation for assessment of lung inflammatory pathology scores. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by the Student t test and two-way ANOVA.
