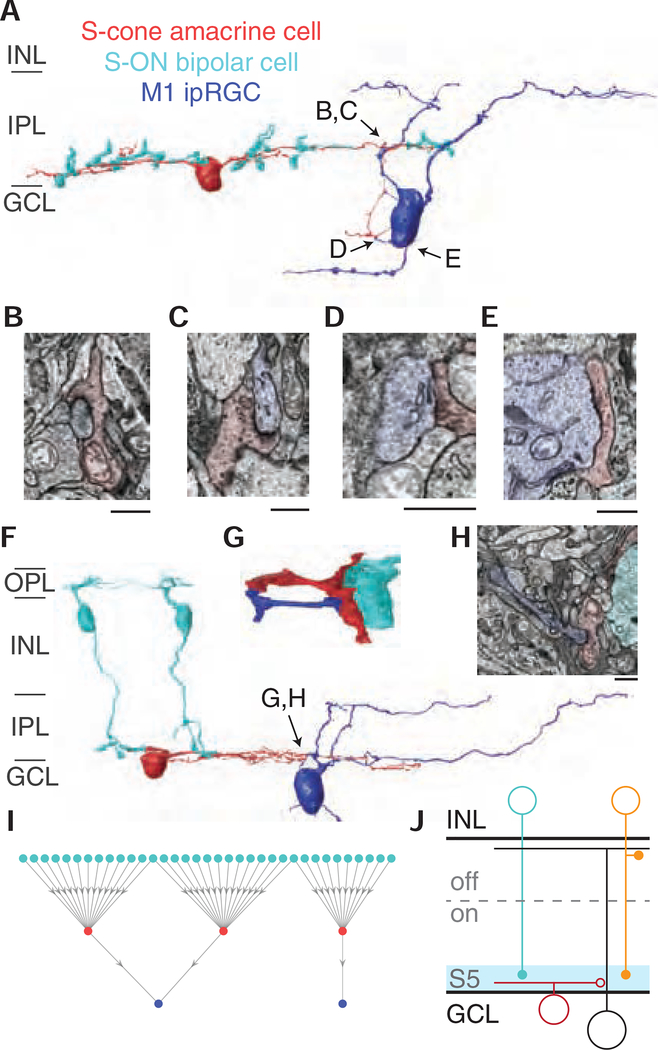
Figure 3. M1 ipRGCs receive targeted inhibitory input from S-cone amacrine cells.
(A) 3D reconstruction of an M1 ipRGC receiving synaptic input from an S-cone amacrine cell. The S-cone amacrine cell dendrite travels into the ganglion cell layer to provide additional synaptic input to the M1 ipRGC soma. See also Video S1. (B-E) Four electron micrographs of the synapses in 3A. (F) 3D reconstruction of S-cone amacrine cell input to an M1 ipRGC, with complete reconstructions of two representative S-ON bipolar cells. (G) Detailed reconstruction of S-cone amacrine cell to ipRGC synaptic contact. (G) Synapse from an S-cone amacrine cell to the M1 ipRGC in 3F and 3H. Scale bar is 1 μm. (I) Network of S-ON bipolar cells, S-cone amacrine cells and M1 ipRGCs. (J) Circuit diagram of cone-opponent inputs to ipRGCs. En passant synapses from ON diffuse bipolar cells (orange) contribute to the LM-ON response [16,43].