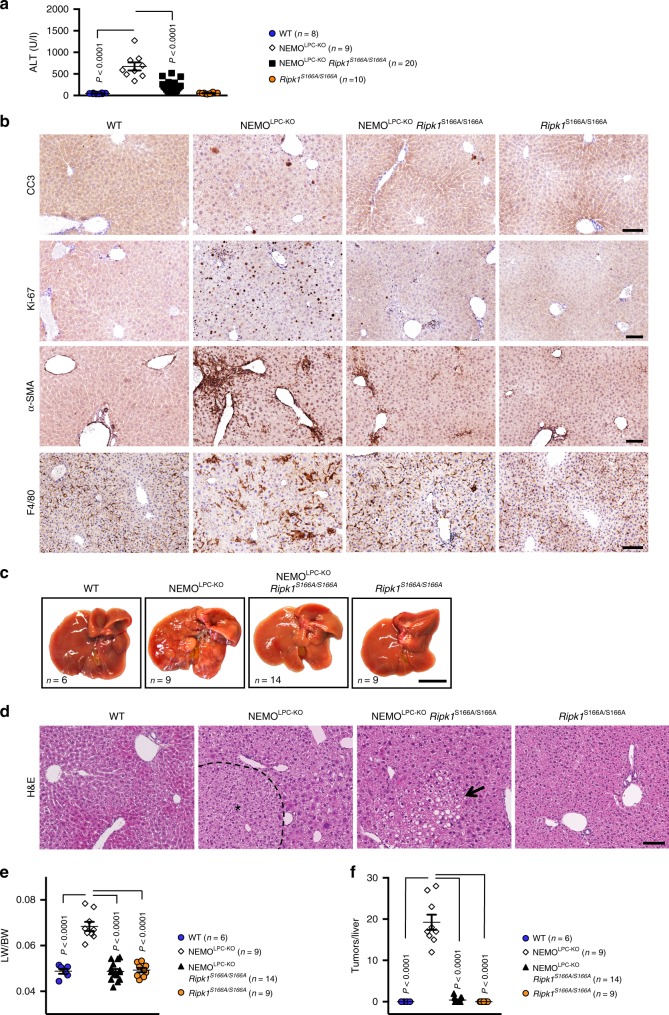
Fig. 4. S166 phosphorylation is essential for RIPK1-dependent hepatitis and liver tumorigenesis in NEMOLPC-KO mice.
a Graph depicting basal serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in 8-week-old mice of the indicated genoytpes. b Representative images of liver sections from 8-week-old mice of the indicated genotypes that were stained with H&E or immunostained with the indicated antibodies. Scale bars, 200 μm. c Representative photographs of livers from 50-week-old mice with the indicated genotypes. Scale bar, 1 cm. d Representative images of liver sections from 50-week-old mice of the indicated genotypes stained with H&E. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) areas are outlined and marked with an asterisk. Arrow points at a small steatotic area observed in some NEMOLPC-KO Ripk1S166A/S166A mice. Scale bars, 200 μm. e Tumor load quantification in 50-week-old mice by liver weight/body weight (LW/BW) ratios. f Graph depicting tumor number per liver for 50-week-old mice of the indicated genotypes. a, e, f The dots in the graphs represent individual mice. Horizontal lines indicate mean values ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA. Source data for a, e, f are provided as source data file.