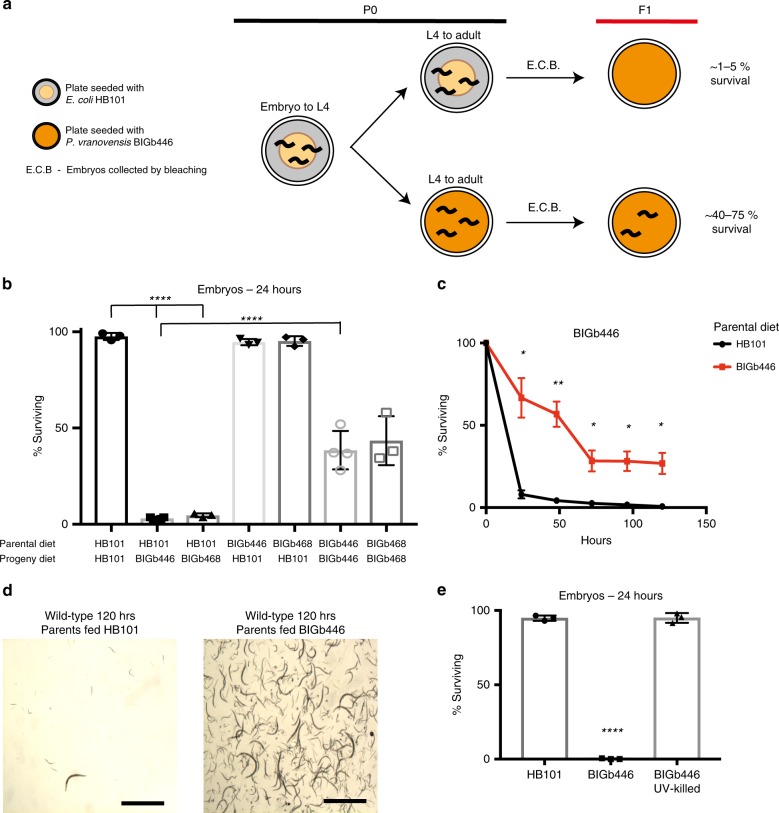
Fig. 1. C. elegans heritably adapts to infection by Pseudomonas vranovensis.
a Graphical representation of experimental set up. Embryos collected by bleaching were placed onto fresh plates seeded with BIGb446 immediately after egg prep and the percent of surviving animals was counted after 24 h. b Percent of wild-type animals surviving on plates seeded with either E. coli HB101 or bacterial isolates BIGb446 and BIGb468 after 24 h. Data presented as mean values ± s.d. n = 3–4 experiments of >100 animals. c Percent of wild-type animals surviving on plates seeded with bacterial isolate BIGb446. Data presented as mean values surviving at each time point from three separate experiments ± s.d. n = 3 experiments of 500 animals. Log-rank test of individual Kaplan–Meier survival curves p < 0.001. d Images of wild-type animals surviving after 120 h of feeding on bacterial isolate BIGb446. 1000 animals were used at t = 0 in each condition and surviving animals were resuspended in 20 μl M9 and imaged. Scale bars 1 mm. Experiment repeated three times with similar results. e Percent of wild-type animals surviving on E. coli HB101 or bacterial isolate BIGb446 after 24 h. Data presented as mean values ± s.d. n = 3 experiments of >100 animals. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. See statistics and reproducibility section for statistical tests run.