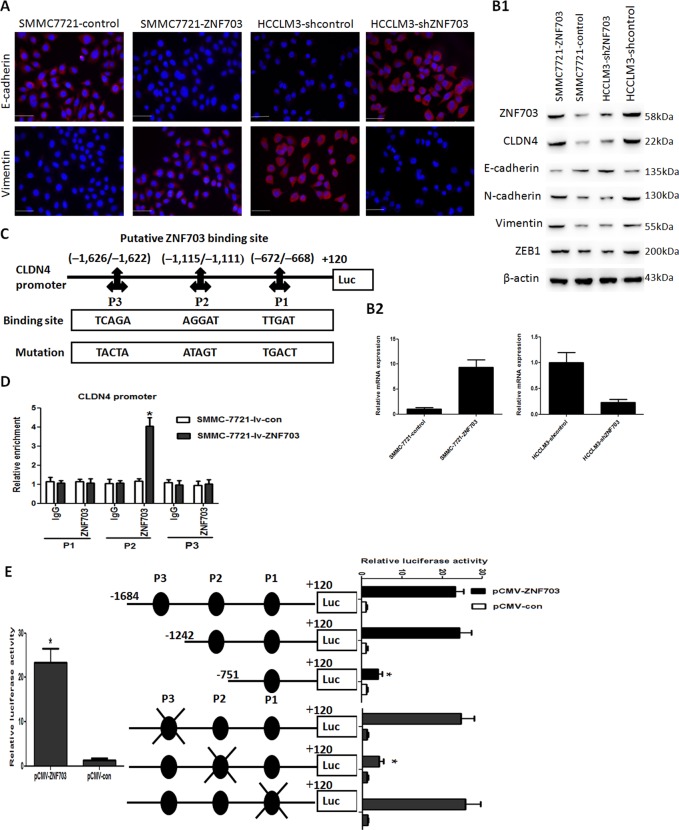
Fig. 3. ZNF703 facilitates hepatoma cell metastasis by transactivating CLDN4 expression.
A Immunofluorescence staining show that decreased expression of an epithelial marker (E-cadherin) and increased expression of a mesenchymal marker (vimentin) in SMMC7721-ZNF703 cell, whereas increased expression of an epithelial marker (E-cadherin) and decreased expression of a mesenchymal marker (vimentin) in HCCLM3-shZNF703 cell. Scale bars: 50 μm. B1 Western blotting analysis of ZNF703, CLDN4, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin, and ZEB1 expression in the SMMC7721-ZNF703 and HCCLM3-shZNF703 cells. B2 Real-time PCR analysis of CLDN4 level in the SMMC7721-ZNF703 and HCCLM3-shZNF703 cells. C Prediction and validation of putative ZNF703-binding sites in the CLDN4 promoter and mutations in corresponding binding sites. D ChIP and real-time PCR assays demonstrate that ZNF703 binds directly to the CLDN4 promoter in SMMC7721-ZNF703 cells. E A luciferase reporter assay shows that ZNF703 apparently forces CLDN4 promoter activity. Deletionand selective mutagenesis are used to determine ZNF703-responsive regions in the CLDN4 promoter. Schematic representations of serially truncated andmutated CLDN4 promoters (left) and the corresponding relative luciferase activity (right) are shown. Data are presented as mean ± S.D for three independent experiments. *P < 0.05.