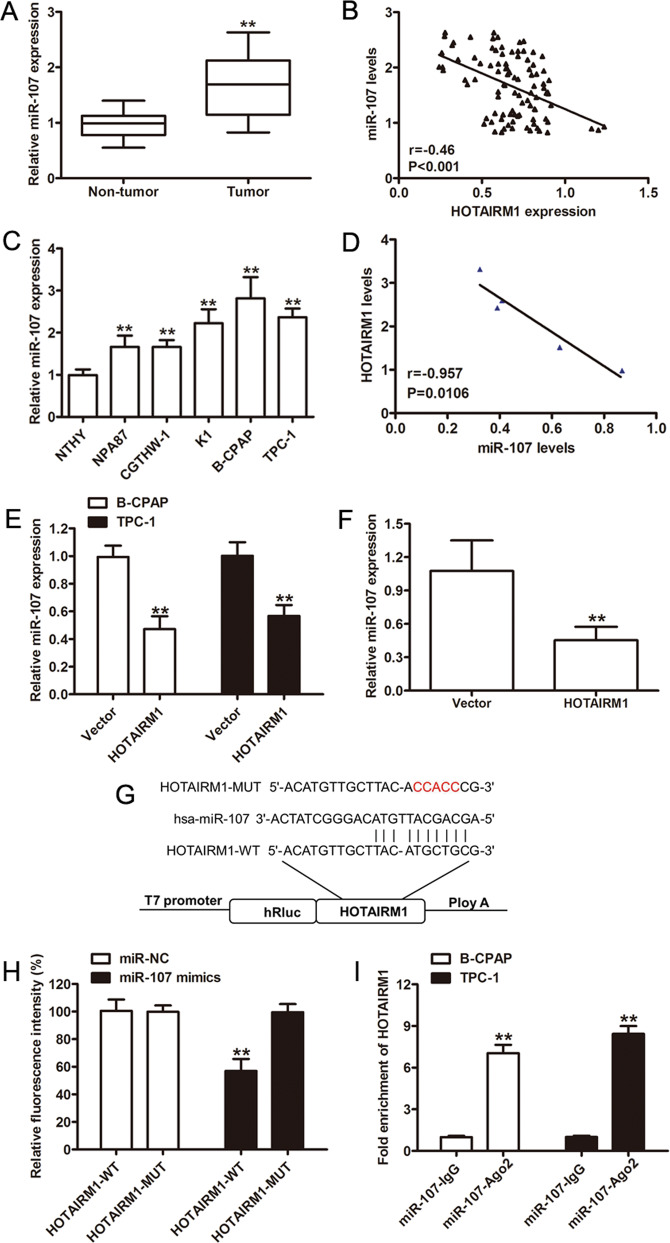
Fig. 4. HOTAIRM1 regulated the expression of miR-107.
a Relative miR-107 expression levels determined by qRT-PCR in PTC samples (n = 96, **p < 0.001). b Negative correlation between HOTAIRM1 and miR-107 levels in 96 paired PTC tissues. c, d Relative expression levels of miR-107 in PTC cell lines (NPA87, CGTHW-1, K1, B-CPAP, and TPC-1) compared in a pairwise manner with expression levels in a normal human thyroid follicular epithelial cell line (Nthy-ori 3-1, n = 3, **p < 0.001). Negative correlations between HOTAIRM1 and miR-107 in the same panel of cell lines. e, f Relatively low miR-107 expression levels detected by qRT-PCR in HOTAIRM1-overexpressing PTC cells (n = 3, **p < 0.001) and in HOTAIRM1-overexpressing xenograft tumor tissues (n = 5, **p < 0.001). g Online bioinformatics software tools predicted a putative binding site between HOTAIRM1 and miR-107 and the binding site was mutated for dual-luciferase reporter assays. h A dual-luciferase reporter gene assay showed that miR-107 decreased the luciferase activity in the HOTAIRM1-WT group (n = 3, **p < 0.001). i RNA immunoprecipitation assay using an anti-Ago2 antibody and an IgG control showed a high degree of HOTAIRM1 enrichment (n = 3, **p < 0.001).