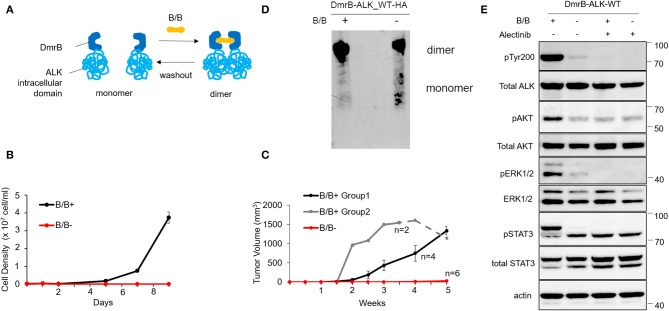
Figure 1.
Effect of conditional monomerization of DmrB-ALK_wt. (A) Illustration of the inducible dimerization of wild-type ALK intracellular domain. ALK intracellular domain encoded by exons 20–29 was ligated to DmrB (DmrB-ALK_wt). Dimer/monomer state of the fusion protein was regulated by B/B homodimerizer (B/B) which acts as a ligand for DmrB. (B) Proliferation of Ba/F3 cells expressing DmrB-ALK_wt (Ba/F3 DmrB-ALK_wt) after B/B withdrawal or B/B continuation. Survival and proliferation of Ba/F3 DmrB-ALK_wt were dependent on B/B continuation. Error bars: SD. (C) Tumor volume curve of Ba/F3 DmrB-ALK_wt xenografts in nude mice. Nude mice were treated with B/B for 5 w (group 1), 3.5 w (group 2, solid line) and then withdrawn for 1.5 w (group 2, dashed line) or mock solution for 5 w. Tumor formation and growth was dependent on continuous B/B treatment. Error bars: SD. (D) Western blotting of the DmrB-ALK_wt protein with an anti-HA antibody. The DmrB-ALK_wt protein was immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody and electrophoretically separated on a native polyacrylamide gel under non-denaturing conditions. Under the B/B treatment, monomeric DmrB-ALK_wt (predicted molecular weight of 75.5 kDa) was not observed (left lane). After withdrawal of B/B, monomeric DmrB-ALK_wt proteins were detected (right lane). (E) Western blotting of Ba/F3 DmrB-ALK_wt with B/B treatment (B/B+) or B/B withdrawal (B/B–). Phosphorylation of ALK, ERK1/2, AKT, and Stat3 proteins were significantly attenuated in the B/B withdrawal condition. Total and phosphorylated proteins were probed on the same blot sequentially.