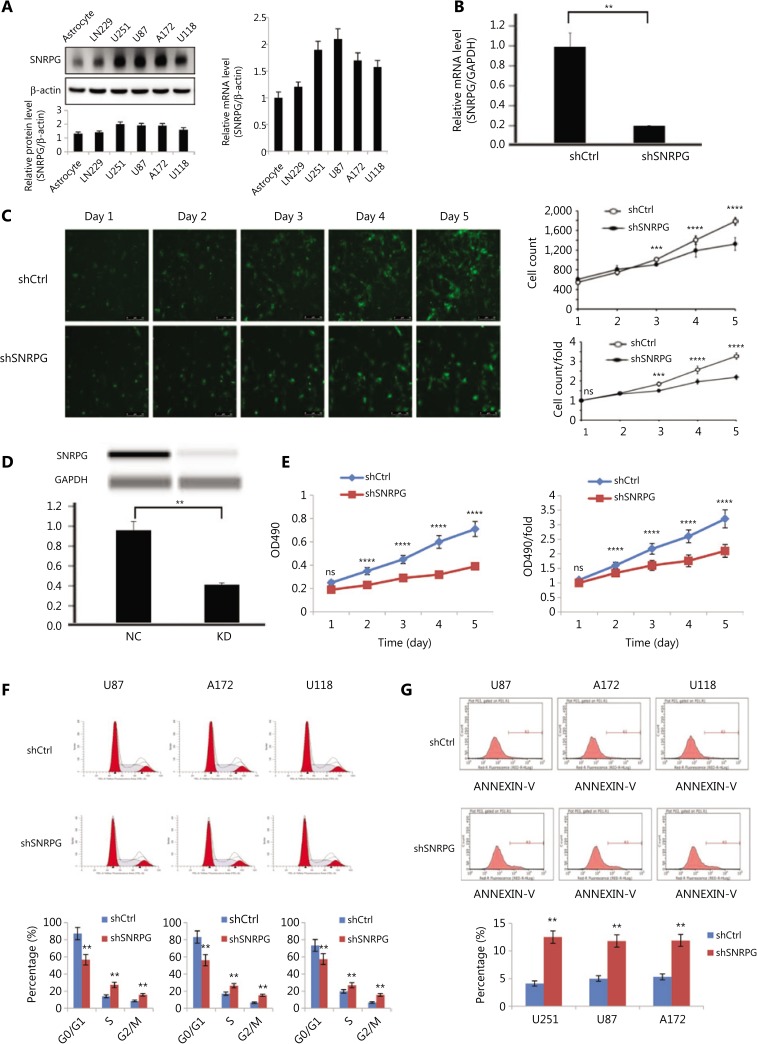
Figure 2.
Effects of SNRPG knockdown on cell proliferation. (A) Expression of SNRPG in normal astrocyte and glioma cell lines detected by Western blot and RT-qPCR. The RT-qPCR results indicated that all glioblastoma cell lines exhibited high expression of SNRPG (mean ± SD, n = 3). The U87MG and U251 cell lines were selected for further study to investigate the biological role of SNRPG in GBM cells. (B) SNRPG was knocked down using shRNA (mean ± SD, n =3, **P < 0.01). (C) The Celigo assay was performed to detect cell viability over 5 days after transfection. The colony numbers of U87MG cells transfected with shCtrl were larger than those of U87MG cells transfected with shSNRPG (mean ± SD, n = 3, ns, not significant; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). Bar = 50 μm. (D) Simple Western lane view with results automatically generated by system software. The downregulated expression of SNRPG by shSNRPG in U87MG cells was further confirmed via a simple Western size assay (**P < 0.01). (E) The MTT assay showed that SNRPG knockdown significantly decreased the proliferation of U87MG cells compared with that of the control cells. The optical density values were measured on the indicated days (mean ± SD, n = 3, ns, not significant; ****P < 0.0001). (F) Flow cytometry analysis was performed to further examine the effect of SNRPG on the proliferation of glioblastoma multiforme cells by altering cell cycle progression. Error bars, standard error. **P < 0.01. (G) To further determine the physiological role of SNRPG in cell growth, U87MG, A172, and U118 cells were transfected with shSNRPG. After 48 h, cell apoptosis was examined by flow cytometry analysis. Graphs show the mean percentages of three biological replicates. Error bars, standard error. **P < 0.01.