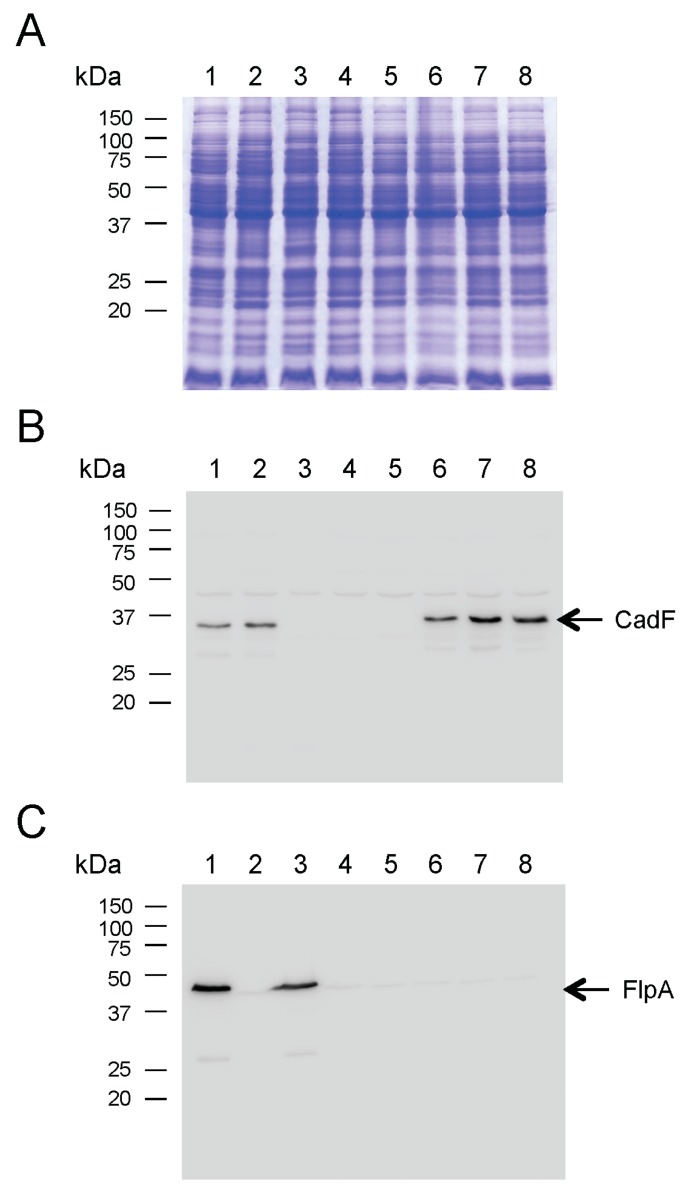
Figure 3.
Electrophoretic and immunoblot analysis of C. jejuni ΔcadF ΔflpA transformants. Bacterial whole-cell lysates were separated in SDS 12.5% polyacrylamide gels and either: (A) stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250, (B) transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes and probed with a rabbit α-CadF serum, or (C) transferred to PVDF membranes and immunoblot with a rabbit α-FlpA serum. The positive control consisted of a C. jejuni wild-type strain. The negative controls consisted of a ΔcadF ΔflpA mutant (lane 4) and the ΔcadF ΔflpA::cadFNP-FLAG isolate (lane 5). The arrows indicate the CadF protein (Panel B) and the FlpA protein (Panel C). Lanes: C. jejuni strains (1) 81-176 (wild-type); (2) ΔflpA; (3) ΔcadF; (4) ΔcadF ΔflpA; (5) ΔcadF ΔflpA::cadFNP-FLAG; (6) ΔcadF ΔflpA::PcadF-283 bp cadF-FLAG; (7) ΔcadF ΔflpA::PcadF-334 bp cadF-FLAG; and (8) ΔcadF ΔflpA::PcadF-400 bp cadF-FLAG. Molecular mass standards (in kDa) are on the left.