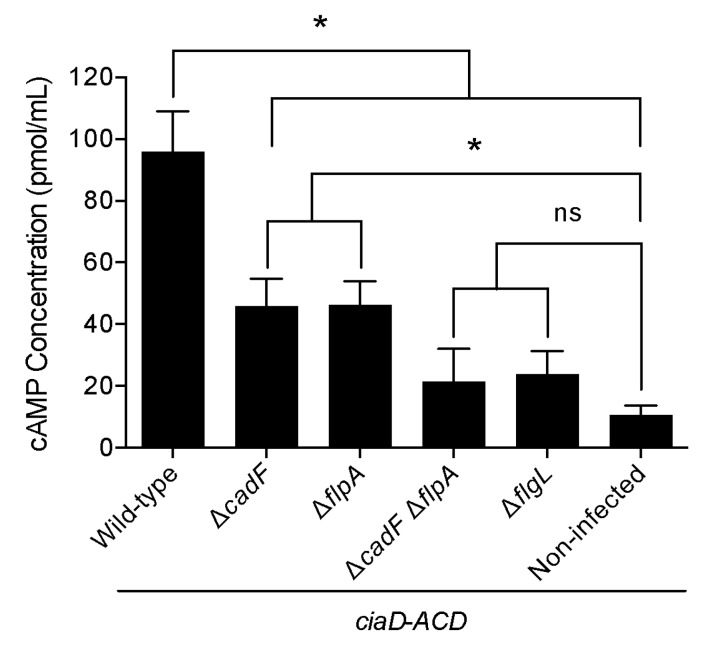
Figure 9.
Efficient delivery of the C. jejuni CiaD effector protein to host cells requires the CadF and FlpA adhesins. A C. jejuni wild-type strain, ΔcadF mutant, ΔflpA mutant, ΔcadF ΔflpA mutant, and ΔflgL mutant (negative control) were transformed with shuttle vector harboring ciaD fused to the adenylate cyclase domain (ciaD-ACD). The delivery of the CiaD-ACD fusion proteins to the cytosol of human INT 407 cells was determined using the adenylate cyclase domain (ACD) delivery assay, as described in the “Materials and Methods” section. The asterisk indicates that the amount of cAMP produced in cells infected with the C. jejuni wild-type strain was significantly greater than the value obtained from a given mutant, as judged by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s analysis (* p< 0.05). The amount of cAMP produced in cells infected with the C. jejuni ΔcadF mutant and ΔflpA mutant was also significantly greater than the non-infected samples (* p< 0.05). The values obtained from the C. jejuni ΔcadF ΔflpA mutant, and ΔflgL mutant showed no statistical significance compared to non-infected samples as judged by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s analysis (* p< 0.05; ns, non-significant). The data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the values from three biological replicates.