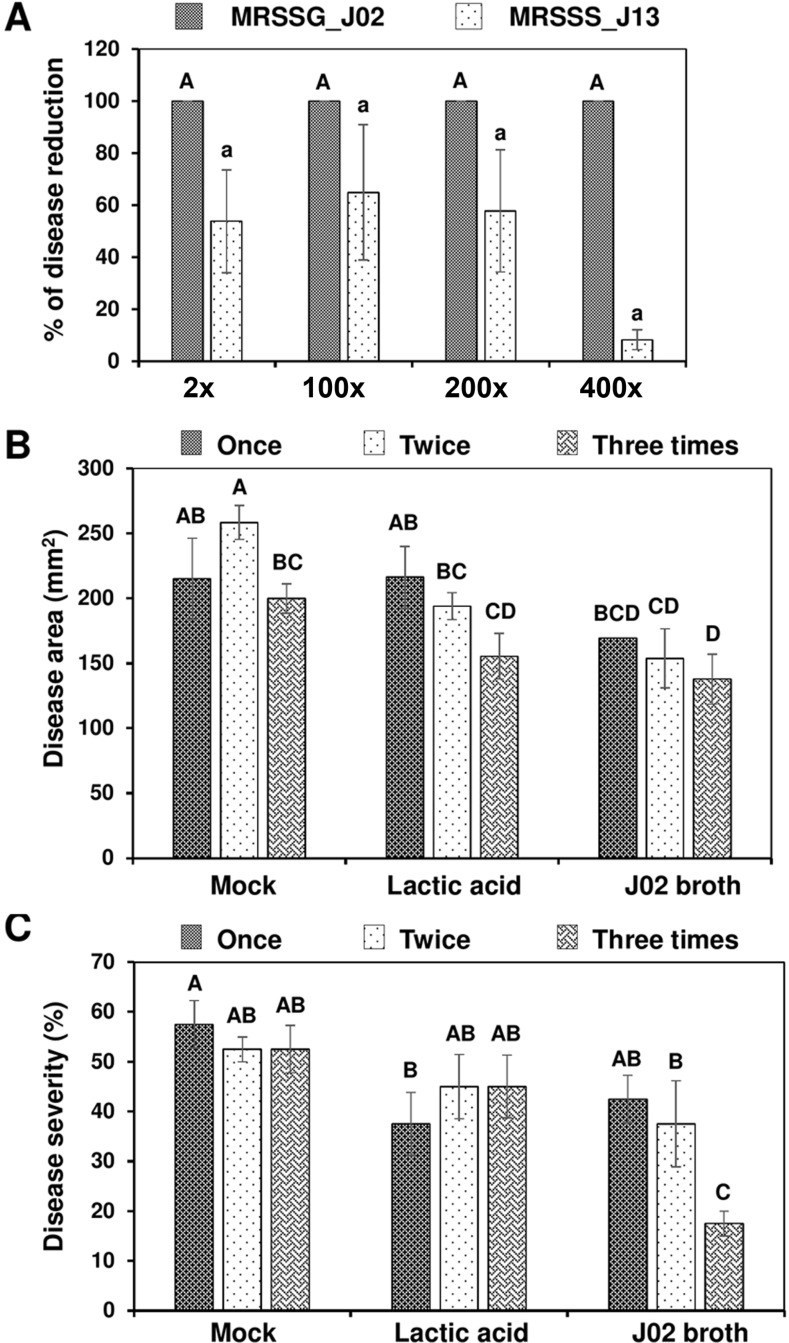
Fig. 6.
Reduction of bacterial disease on cabbage leaves after applying J02 or J13 broth mixing with chitosan. (A) Reduction of soft rot on cabbage leaves. J02 and J13 were cultured in MRSSG (a modified De Man, Rogosa and Sharpe medium containing surimi and glycerol, pH 4.1) and MRSSS (MRS containing 1.5% surimi and 0.5% sucrose, pH 5.3), respectively, diluted, and mixed with 1% chitosan. The resultant solution was mixed with Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum cell suspensions (108 colony-forming unit [cfu]/ml) and applied to longitudinal section of leaf petioles. The treated leaves were maintained in a plastic box for 2 days. (B) Reduction of black rot caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc) on cabbage leaves after being sprayed with J02 broth cultures plus chitosan and inoculated with Xcc using a scissor-cutting method. (C) Reduction of black rot on cabbage seedlings after being sprayed with J02 broth cultures plus chitosan and inoculated with Xcc using a spraying method. J02 broth and chitosan were sprayed on to cabbage seedlings at day 28 (one application), days 21 and 28 (two applications), or days 14, 21, and 28 (three applications) and inoculated with Xcc suspensions (108 cfu/ml) at day 29. Plants treated with water (mock) or 2% lactic acid were used as the controls. Means followed by the same case letters in each panel were not significantly different (P ≤ 0.05).