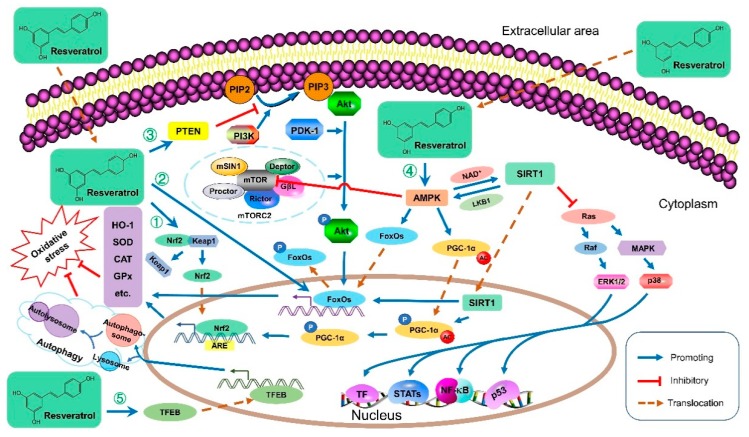
Figure 1.
The antioxidant molecular mechanisms of resveratrol. ① Resveratrol unanchors Nrf2 in the cytoplasm, disrupting its Keap1-dependent ubiquitination and degradation. The built-up Nrf2 translocates into the nucleus, binds to ARE, and initiates the transcription of many antioxidative genes such as SOD and CAT to reduce oxidative stress. ② Resveratrol promotes the transcriptional functions of FoxOs in the nucleus to facilitate the transcription of many antioxidative genes like HO-1, contributing to the reduction of oxidative stress. ③ Resveratrol upregulated PTEN, a major antagonist of PI3K, blocking the Akt activation. Consequently, the activated Akt reduces, leading to decreased FoxOs phosphorylation. Therefore, less p-FoxOs translocate from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and more FoxOs remain in the nucleus to act as transcriptional factors. ④ Resveratrol activates AMPK to maintain the structural stability of FoxOs, facilitate its translocation, and accomplish its transcriptional function. In addition, the activated AMPK phosphorylates PGC-1α, which can translocate into the nucleus, and be deacetylated by SIRT1. Then PGC-1α promotes Nrf2, leading to increased antioxidative gene expression and then reduced oxidative stress. Resveratrol activates AMPK, leading to SIRT1 activation, which inhibits MAPK signaling pathways and results in autophagy. ⑤ Resveratrol induces autophagy by activating TFEB, which promotes the formation of autophagosome and lysosome as well as their fusion into an autolysosome, leading to reduced oxidative stress. Abbreviations: AC, acetyl; Akt, protein kinase B; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ARE, antioxidant response element; CAT, catalase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FoxO, forkhead box protein O; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GβL, G protein β subunit-like; HO-1, heme oxygenase 1; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; LKB1, liver kinase B1; MAP2K, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; mSIN1, mammalian stress-activated protein kinase interacting protein 1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; mTORC2, mTOR Complex 2; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Nrf2, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2; P, phosphorylation; p53, phosphoprotein p53; PDK1, phosphoinositide dependent kinase 1; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; Rictor, the rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; SOD, superoxide dismutase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TF, transcription factor; TFEB, transcription factor EB.