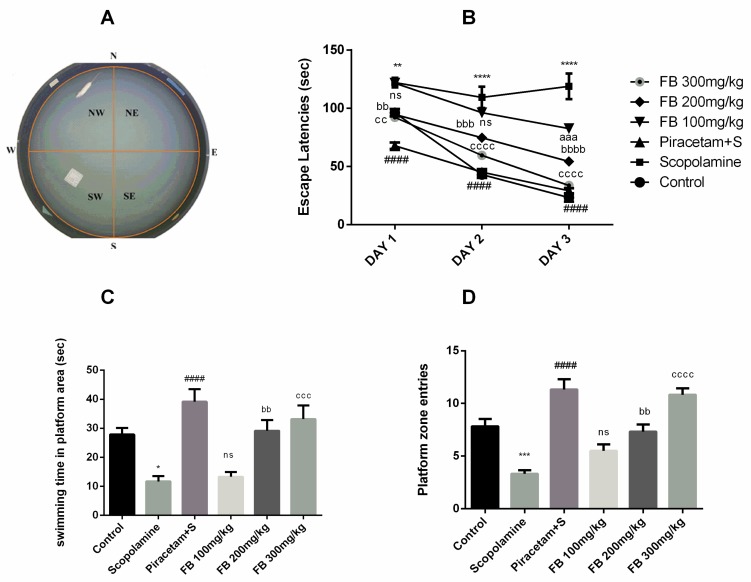
Figure 4.
Display of proximal cues in Morris water maze (MWM) tank (A), impact of FB bark extract (100, 200 and 300 mg/kg) on scopolamine (2 mg/kg, i.p.) treated rats on escape latencies from day 1 to 3 (B), swimming time in platform area (C) and platform zone entries (D) on probe day using piracetam as positive control. Data are presented as ± SEM (n = 6 per group). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 comparison between control (vehicle-treated) and scopolamine group, #### p < 0.0001 comparison between scopolamine and piracetam treated groups. aaa p < 0.001 comparison between scopolamine and FB 100 mg/kg treated groups. bb p < 0.01, bbb p < 0.001, bbbb p < 0.0001 comparison between scopolamine and FB 200 mg/kg treated groups. cc p <0.01, ccc p < 0.001, cccc p < 0.0001 comparison between scopolamine and FB 300 mg/kg treated groups. ns not significant.