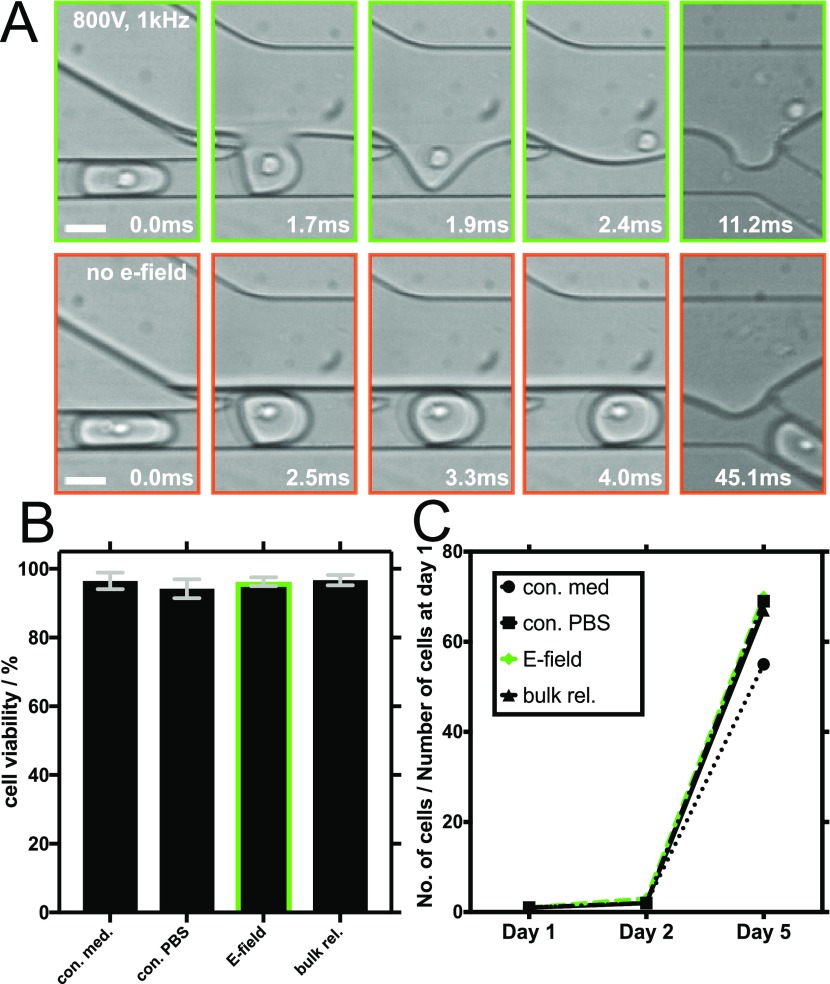
Figure 2.
Electric field-mediated release of encapsulated CHO suspension cells and an assessment of their long-term viability. (A) Representative brightfield images obtained with a high-speed camera showing different time points during cell release: electric field-mediated release (800 V, 1 kHz) is shown in the upper row (green frames) and release without an electric field in the lower row (orange frames). The white scale bars are 30 μm. (B) Results of trypan blue live/dead cell viability assays performed on CHO cells in PBS after their electric field-mediated release (E-field) and on control cells that were left untouched in PBS (con. PBS). Control experiments also included cells cultured in cell medium conditions without employment in microfluidic experiments (con. med) and cells cultured in PBS, encapsulated, and then released in bulk using a destabilizing surfactant (bulk.rel). The green bordered bar shows cell viability after the electric field-mediated release. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of three independent live/dead viability assays of each sample. (C) Summary of 5 day CHO cell proliferation assays following the electric field-mediated release and the control culturing conditions.