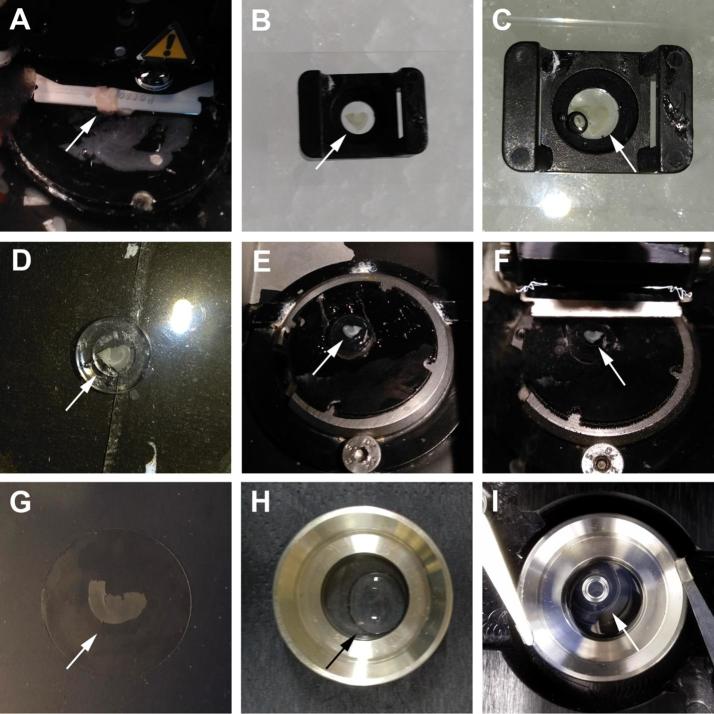
Fig. 1.
Tissue preparation for super-resolution imaging. (A) Acute, 350 μm brain sections are cut from a P160, male C57BL/6J mouse using a vibratome. (B) The sections are flattened out on a glass slide on ice. (C) 2% melted agarose is used to immobilise the tissue during reslicing. (D and E) The embedded tissue is glued to a vibratome stage. (F) The tissue is resliced into 30 μm sections. (G) For imaging, brain sections are placed on top of a coverslip. (H) Melted 2% agarose is used to immobilize the tissue. (I) The imaging chamber is filled with buffer, a coverslip is used to seal the chamber and the chamber is placed into the microscope for imaging. The arrows are pointing towards the tissue.