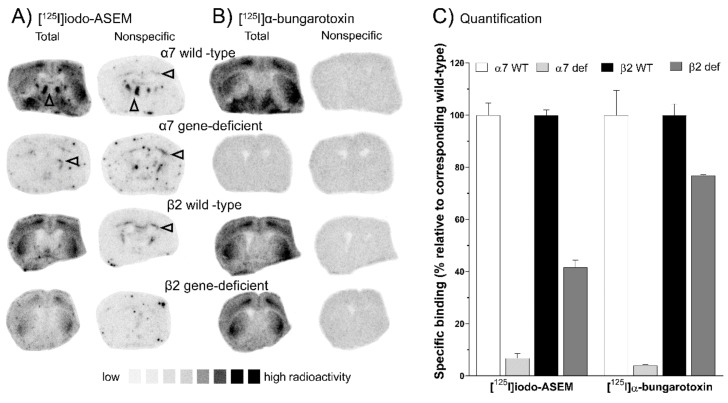
Figure 2.
(A,B) Representative autoradiographs showing total [125I]Iodo-ASEM (A) and [125I]a-bungarotoxin (B) and non-specific (determined with 1 mMol/L (-)-nicotine for [125I]α-bungarotoxin and 10 µMol/L SSR-180,711 for [125I]Iodo-ASEM) binding in 12 µm brain sections of α7 and β2 nAChR wild-type vs. corresponding gene-deficient (def) mice (n = 1 each). Arrowheads indicate residual white matter binding. (C) Comparative quantitative analysis of specific binding (± S.E.M.) of [125I]Iodo-ASEM and [125I]a-bungarotoxin in α7 and β2 nAChR wild-type vs. corresponding gene-deficient mice (n = 1). All autoradiographic experiments and quantifications are carried out in 3-6 sections per animal.