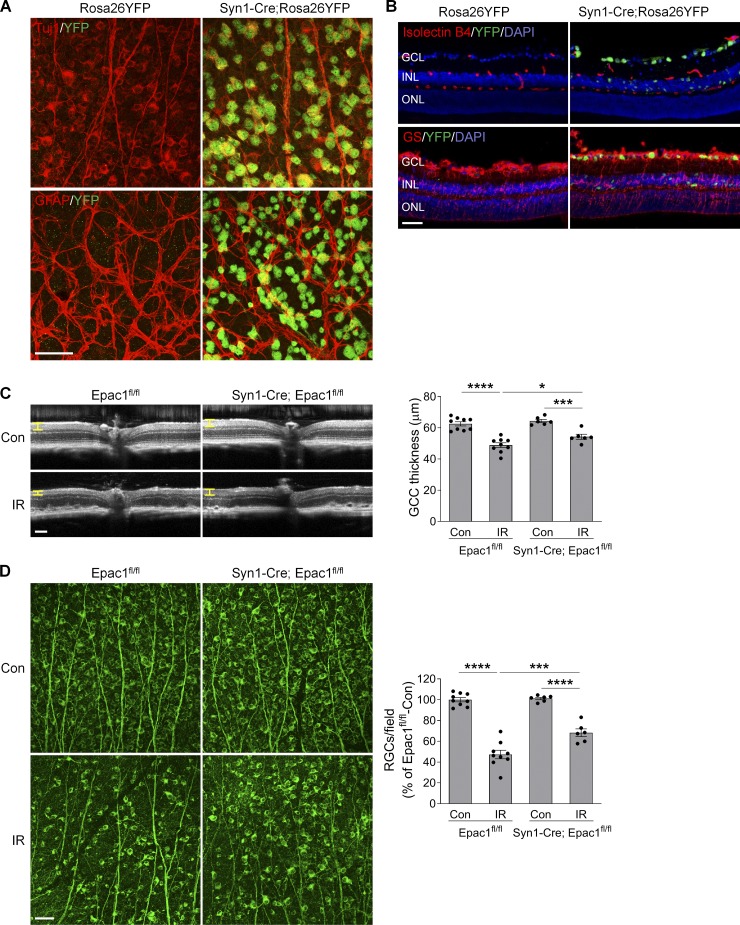
Figure 7.
Epac1 deletion in neurons alleviates RGC death after IR injury. (A and B) Syn1-Cre mice were crossed with Rosa26YFP reporter mice to generate Syn1-Cre; Rosa26YFP mice. Retinal flatmounts (A) or sections (B) were stained with antibodies against YFP (green) and different retinal cell markers (red). Tuj1 for RGCs; GFAP for astrocytes; isolectin B4 for vessels; and glutamine synthetase (GS) for glia (astrocytes and Müller cells). Blue, DAPI staining for nuclei. (C) OCT analysis in live Epac1fl/fl and Syn1-Cre; Epac1fl/fl mice (C57BL/6 background) for retinal thickness 7 d after IR. Yellow H lines indicate the thickness of GCC. Bar graph represents the thickness of GCC. n = 6–9 mice. Scale bar: 100 µm. (D) Representative images of retinal flatmounts labeled with Tuj1 antibody (green) in Epac1fl/fl and Syn1-Cre; Epac1fl/fl mice 7 d after IR. Scale bar: 50 µm. Bar graph represents the percentage of Tuj1-positive cells per field relative to Epac1fl/fl control. n = 6–9 mice; eight images were taken at the peripheral retina for each sample and calculated as average value. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA. Error bars represent SEM.