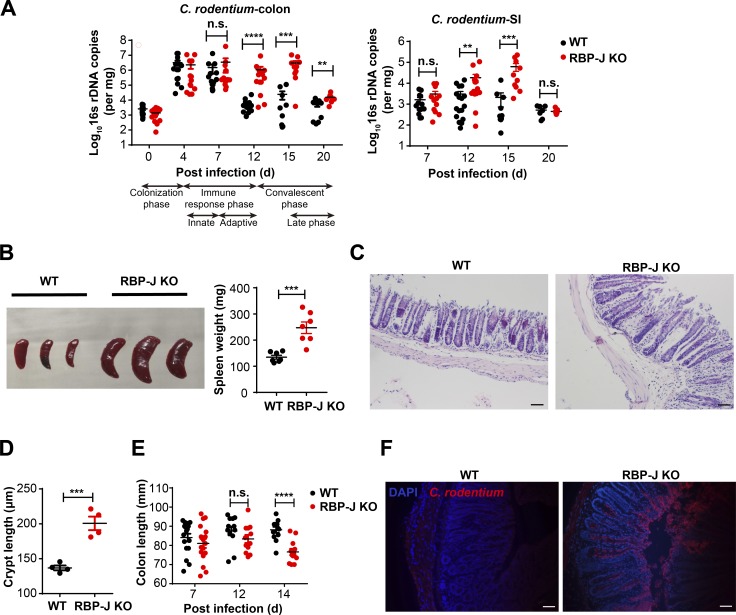
Figure 1.
Myeloid-specific RBP-J deficiency compromises host defense against C. rodentium. 6–8-wk-old WT (Lyz2-Cre) and RBP-J KO (Rbpjfl/fl Lyz2-Cre) mice were orally inoculated with 2 × 109 CFUs of C. rodentium, and tissues were harvested at the indicated time points p.i. (A) qPCR analysis of 16s rDNA copies to determine fecal bacterial burdens in colon (left) and small intestine (SI; right) at the indicated p.i. days. (B) Representative splenomegaly (left) and spleen weights (right) at day 14 p.i. (C and D) Histopathology (C) and crypt lengths (D) in the distal colon at day 14 p.i. (H&E; scale bars represent 50 µm). (E) Measurements of colon lengths at the indicated p.i. days. (F) Visualization of C. rodentium (red) and DAPI (blue) in the distal colon at day 12 p.i. (scale bars represent 50 µm). Data are representative of two independent experiments (B [left], C, D, and F) or pooled from two (B [right]) or four independent experiments (A and E); n ≥ 3 in each group. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n.s., not significant; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; two-tailed Mann-Whitney test (A) or two-tailed Student’s unpaired t test (all other panels). Each symbol represents an individual mouse.