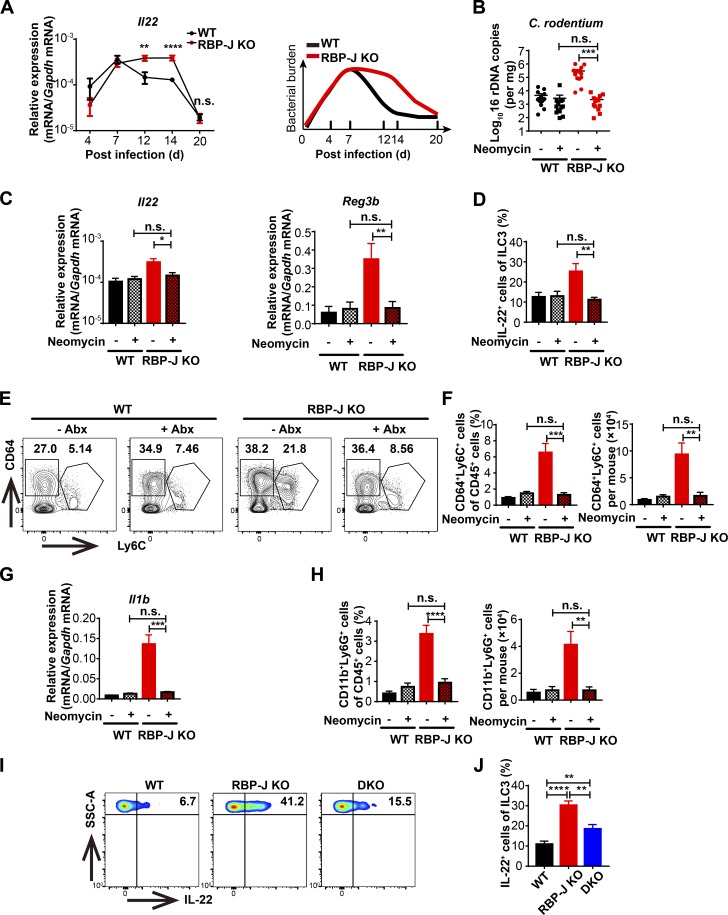
Figure 7.
Persistent IL-22 activities manifest by RBP-J deficiency are dependent on noneradicated pathogens-elicited CD64+Ly6C+ colonic macrophages. (A) qPCR of Il22 in colon tissues (left) and schematic illustration of bacterial burdens in colon (right) from WT and RBP-J KO mice at the indicated p.i. days. Data are pooled from three independent experiments; n ≥ 3 in each group. (B–H) 6–8-wk-old mice were orally inoculated with 2 × 109 CFUs of C. rodentium and given neomycin sulfate individually at day 12 p.i., and mice were sacrificed at day 14 p.i. Data are pooled from three independent experiments; n ≥ 3 in each group. (B) qPCR analysis of 16s rDNA copies to determine fecal bacterial burdens in colon with or without neomycin treatment. (C) qPCR of Il22 and AMPs in colon tissues with or without neomycin treatment. (D) FACS cumulative data of IL-22–producing LP ILC3 (gated by CD45midCD3−Thy-1+) with or without neomycin treatment. (E and F) Representative FACS plots (E) and cumulative data (F) of CD64+Ly6C+ colonic macrophages with or without neomycin treatment. (G) qPCR of Il1b in colon tissues with or without neomycin treatment. (H) FACS cumulative data of LP neutrophils with or without neomycin treatment. (I and J) 6–8-wk-old mice were orally inoculated with 2 × 109 CFUs of C. rodentium. Representative FACS plots (I) and cumulative data (J) of IL-22 production in colonic LP ILC3 (gated by CD45midCD3−Thy-1+) at day 14 p.i. Data are pooled from three independent experiments; n ≥ 3 in each group. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n.s., not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; two-tailed Mann-Whitney test (B) or two-tailed Student’s unpaired t test (other panels). Each symbol in B represents an individual mouse. SSC-A, side scatter area.