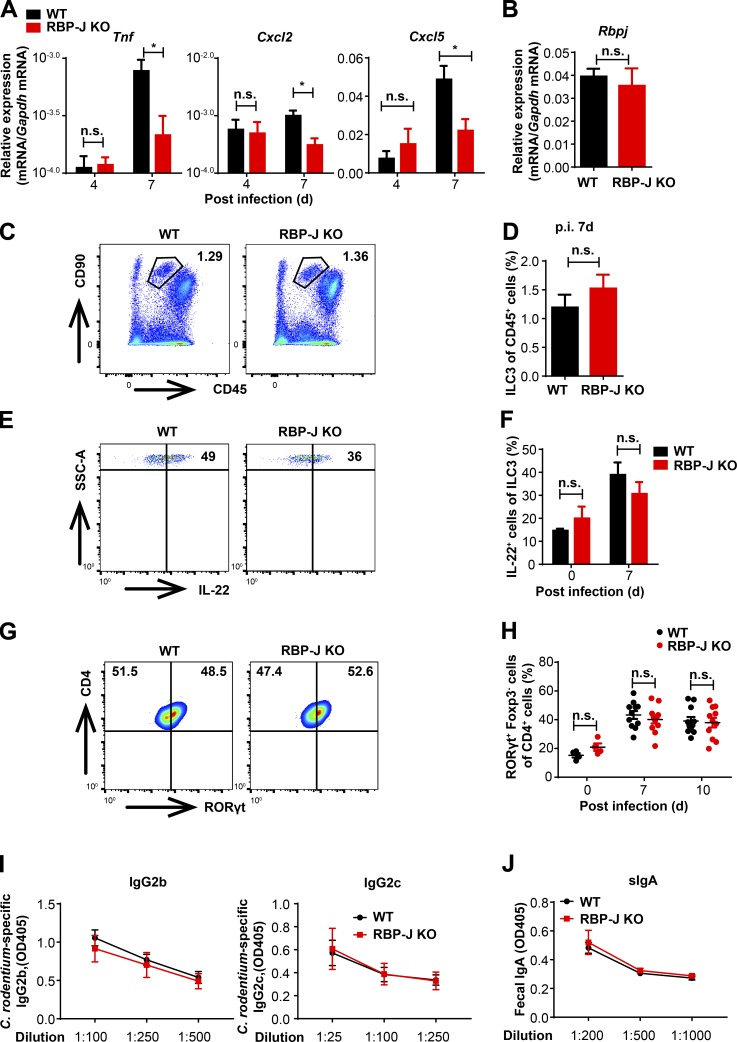
Figure S2.
RBP-J KO mice display normal activation of ILC3 and humoral immune responses during the adaptive immune response phase against C. rodentium infection. (A) 6–8-wk-old WT and RBP-J KO mice were orally inoculated with 2 × 109 CFUs of C. rodentium, and colons were harvested at the indicated time points p.i. qPCR analysis of the indicated mRNAs in colon tissues is shown. Data are pooled from two independent experiments; n = 3 in each group. (B) qPCR of Rbpj in sorted LP CD4+ T cells from uninfected mice. Data are pooled from two independent experiments; n = 3 in each group. (C–H) Representative FACS plots of colonic LP ILC3 (CD45midCD3−Thy-1+), IL-22–producing ILC3 and Th17 cells (CD3+CD4+RORγt+) at day 7 p.i. (C, E, and G) and cumulative data (D, F, and H). Data are pooled from two independent experiments; n ≥ 3 in each group. (I and J) Serum anti–C. rodentium immunoglobulin G2b (IgG2b) and IgG2c titers (I) and fecal secretory IgA (sIgA) titers (J) at day 12 p.i. were measured by ELISA. Data are pooled from two independent experiments; n = 3 in each group. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; two-tailed Student’s unpaired t test. n.s., not significant; SSC-A, side scatter area.