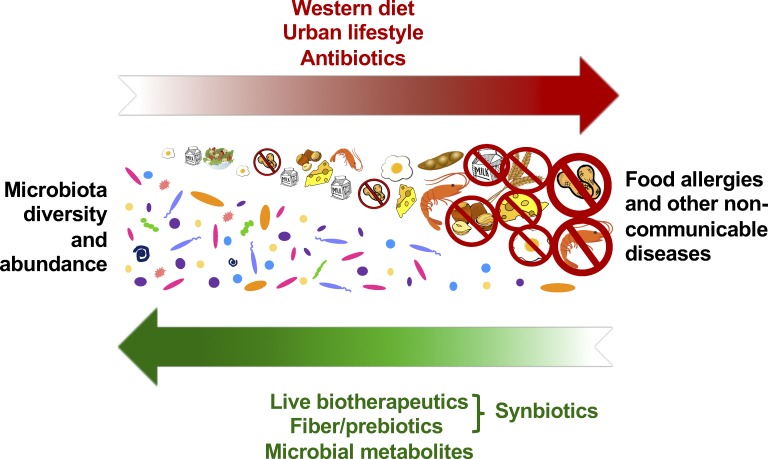
Figure 1.
Decreased microbial diversity and abundance are causal to the increasing prevalence of food allergies and other noncommunicable diseases. Modern lifestyle factors including antibiotic use, urban housing, and Western diet have depleted populations of gut bacteria, such as butyrate-producing Clostridia, that perform barrier-protective functions critical to the maintenance of both physiological and immunological homeostasis. Reintroduction of selected bacterial taxa or their metabolites, particularly in the context of fiber and prebiotics, may restore mucosal function to prevent or treat disease.