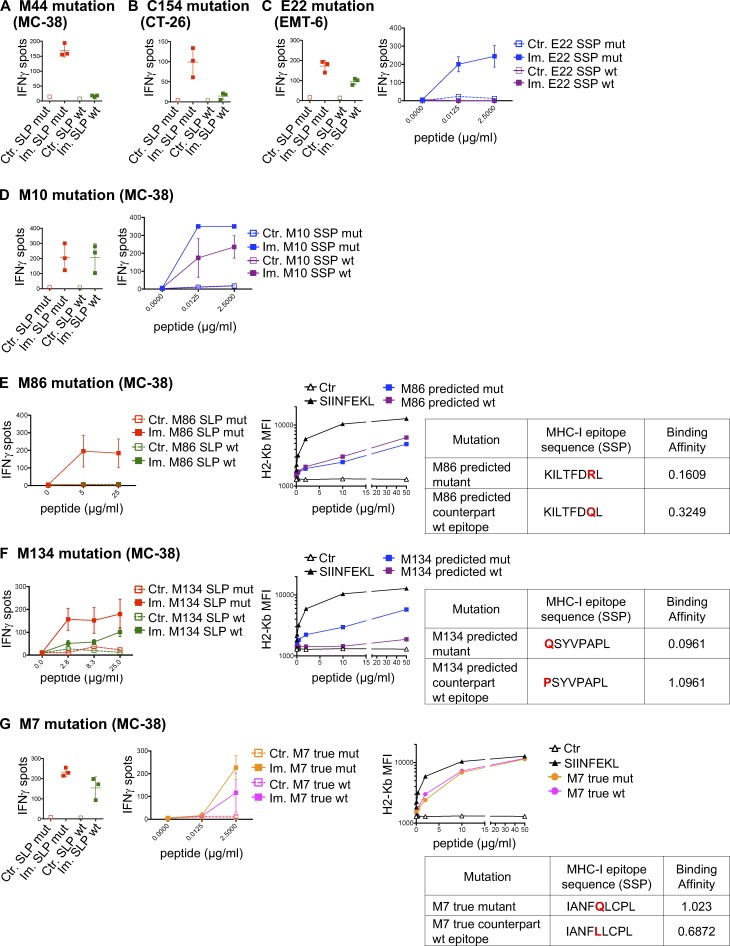
Figure 3.
Cross-reactivity between MHC-I mutant and WT counterpart neoantigens. (A–G) Representative data of mean ± SD IFN-gamma spot numbers from CD8 T cells (5 × 105 CD4-depleted splenocytes/well) from control mice (Ctr., n = 1) or mice immunized with mutant SLPs (Im., n = 3) as depicted in Fig. 1 B, after in vitro restimulation with the mutant SLP or its WT counterpart (25 µg/ml; A-M44 mutation, MC-38; B-C154 mutation, CT-26; C-E22 mutation, EMT-6; D-M10 mutation, MC-38; E-M86 mutation, MC-38; F-M134 mutation, MC38; and G-M7 mutation, MC-38) or with the predicted mutant optimal epitope SSP or its WT counterpart (C, D, and G). Binding assay of the optimal mutant and its WT counterpart SSPs to H-2Kb on Tap-1 KO EL-4 cells is shown, as well as the sequence and the BA (percentile rank) of the predicted optimal epitopes (E–G). Each experiment was performed twice independently.