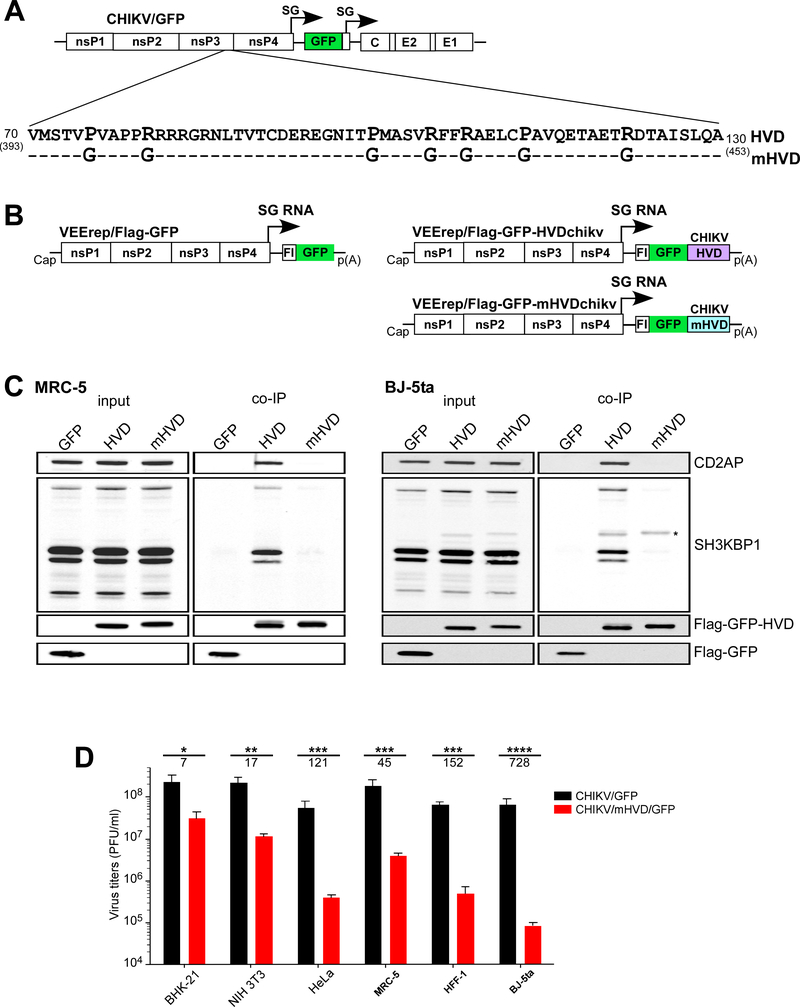
Fig. 6. Mutation is Site 1 and Site 2 of CHIKV HVD abolish binding of CD2AP and SH3KBP1 and strongly inhibit viral replication.
(A) The schematic presentation of CHIKV/GFP genome and mutations introduced into CD2AP-binding sites of CHIKV HVD. Dashes indicate identical aa. (B) The schematic presentation of the designed VEEV replicons, which encoded Flag-GFP alone, and wt and mutant HVDs fused with Flag-GFP. (C) Human MRC-5 and BJ-5ta cells were infected with VEEV replicons encoding Flag-GFP, or Flag-GFP fused with either wt or mutant CHIKV HVD. Protein complexes were isolated using magnetic beads with anti-Flag MAbs and further analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies. An asterisk marks the nonspecific staining of Flag-GFP-HVDs. (D) Equal numbers of indicated cells in the wells of 6-well plate were infected with the indicated viruses at an MOI of 0.04 PFU/cell. After incubation for 15 h at 37° C, media were harvested, and viral titers were determined by plaque assay on BHK-21 cells. Significances of differences among the values were determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test (*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; ****, P<0.0001; n=3). Data are presented as mean with SD (n=3). Numbers under asterisks indicate average fold differences between the titers.