FIGURE 6.
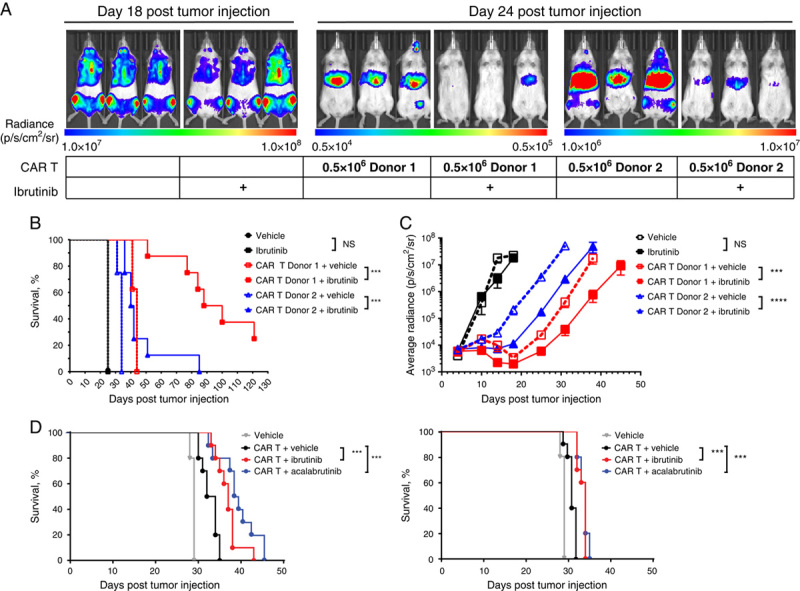
Ibrutinib and acalabrutinib enhanced CD19-directed CAR T-cell–mediated antitumor activity in the disseminated Nalm-6 tumor model. A, Nalm-6 tumor-bearing NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIL-2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice were treated daily with PO ibrutinib 25 mg/kg. A suboptimal dose of 0.5×106 CAR T cells/mouse was transferred intravenously into mice 5 days posttumor injection. N=10 mice per group. Representative bioluminescence images of mice at day 18 (no CAR T-cell treatment mice) and day 24 posttumor transfer. Scales indicate the levels of radiance measured (p/s/cm2/sr) for each group of mice. B, Kaplan-Meier curves showing the survival of tumor-bearing mice treated with PO ibrutinib 25 mg/kg and CAR T cells from 2 different donors. C, Tumor growth over time as indicated by measuring average radiance by bioluminescence from mice treated with PO ibrutinib 25 mg/kg and CAR T cells from 2 different donors. D, Kaplan-Meier curves showing the survival of tumor-bearing mice treated with ibrutinib or acalabrutinib in drinking water (equivalent to PO dose of 25 mg/kg/d) and CAR T cells from 2 different donors. N=8 mice per group were monitored for tumor burden. Statistically significant differences are indicated as ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001. CAR indicates chimeric antigen receptor; NS, not significant; p/s/cm2/sr, photons per second per centimeter squared per steradian; PO, oral.
