Figure 1.
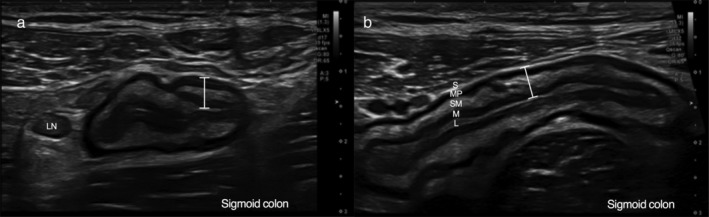
Colonic inflammation detected using point‐of‐care gastrointestinal ultrasound. (a) Transverse section of inflamed sigmoid colon in a patient with Crohn's colitis characterized by increased wall thickness (5.5 mm, measured using marker), abnormal wall stratification with submucosal prominence, and an enlarged lymph node within mesenteric hyperechogenicity reflective of fibrofatty proliferation. Note that Doppler signal is not shown. (b) Longitudinal section of same inflamed sigmoid colon in a patient with Crohn's colitis with a marker again showing increased wall thickness (5.5 mm). The bowel wall layers are annotated: L, luminal interface, white; M, mucosa, black; SM, submucosa, white; MP, muscularis propria, black; S, serosa, white. Note that Doppler signal is not shown.
